Wnt signaling in cancer
- PMID: 22438566
- PMCID: PMC3331705
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008052
Wnt signaling in cancer
Abstract
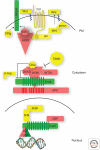
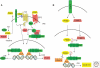
Aberrant regulation of the Wnt signaling pathway is a prevalent theme in cancer biology. From the earliest observation that Wnt overexpression could lead to malignant transformation of mouse mammary tissue to the most recent genetic discoveries gleaned from tumor genome sequencing, the Wnt pathway continues to evolve as a central mechanism in cancer biology. This article summarizes the evidence supporting a role for Wnt signaling in human cancer. This includes a review of the genetic mutations affecting Wnt pathway components, as well as some of epigenetic mechanisms that alter expression of genes relevant to Wnt. I also highlight some research on the cooperativity of Wnt with other signaling pathways in cancer. Finally, some emphasis is placed on laboratory research that provides a proof of concept for the therapeutic inhibition of Wnt signaling in cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Araki Y, Okamura S, Hussain SP, Nagashima M, He P, Shiseki M, Miura K, Harris CC 2003. Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by the Wnt and ras pathways. Cancer Res 63: 728–734 - PubMed
-
- Ashihara E, Kawata E, Nakagawa Y, Shimazaski C, Kuroda J, Taniguchi K, Uchiyama H, Tanaka R, Yokota A, Takeuchi M, et al. 2009. β-catenin small interfering RNA successfully suppressed progression of multiple myeloma in a mouse model. Clin Cancer Res 15: 2731–2738 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
