Oncogenic activation in prostate cancer progression and metastasis: Molecular insights and future challenges
- PMID: 22438770
- PMCID: PMC3307249
- DOI: 10.4103/1477-3163.93001
Oncogenic activation in prostate cancer progression and metastasis: Molecular insights and future challenges
Abstract
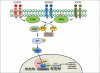
Prostate cancer is a leading cause of death among men in the United States, and currently early diagnosis and appropriate treatment remain key approaches for patient care. Molecularly prostate cancer cells carry multiple perturbations that generate malignant phenotype capable of uncontrolled growth, survival, and invasion-metastasis to other organs. These alterations are acquired both by genetic and epigenetic changes in tumor cells resulting in the activation of growth factor receptors, signaling proteins, kinases, transcription factors and coregulators, and multiple proteases required for the progression of the disease. Recent advances provide novel insights into the molecular functions of these oncogenic activators, implicating potential therapeutic targeting opportunities for the treatment of prostate cancer.
Keywords: PI3K-Akt; Prostate cancer; growth factor receptors; oncogene; proteases; signaling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Signoretti S, Montironi R, Manola J, Altimari A, Tam C, Bubley G, et al. Her-2-neu expression and progression toward androgen independence in human prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:1918–25. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA, Holt JA, Wong SG, Keith DE, et al. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989;244:707–12. - PubMed
-
- Sliva D. Signaling pathways responsible for cancer cell invasion as targets for cancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2004;4:327–36. - PubMed
-
- Pollak MN, Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE. Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:505–18. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

