Amyloid-like fibril formation by polyQ proteins: a critical balance between the polyQ length and the constraints imposed by the host protein
- PMID: 22438863
- PMCID: PMC3305072
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031253
Amyloid-like fibril formation by polyQ proteins: a critical balance between the polyQ length and the constraints imposed by the host protein
Abstract
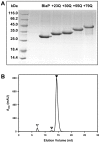
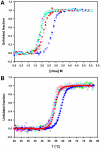
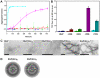
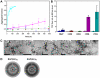
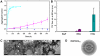
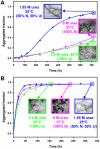
Nine neurodegenerative disorders, called polyglutamine (polyQ) diseases, are characterized by the formation of intranuclear amyloid-like aggregates by nine proteins containing a polyQ tract above a threshold length. These insoluble aggregates and/or some of their soluble precursors are thought to play a role in the pathogenesis. The mechanism by which polyQ expansions trigger the aggregation of the relevant proteins remains, however, unclear. In this work, polyQ tracts of different lengths were inserted into a solvent-exposed loop of the β-lactamase BlaP and the effects of these insertions on the properties of BlaP were investigated by a range of biophysical techniques. The insertion of up to 79 glutamines does not modify the structure of BlaP; it does, however, significantly destabilize the enzyme. The extent of destabilization is largely independent of the polyQ length, allowing us to study independently the effects intrinsic to the polyQ length and those related to the structural integrity of BlaP on the aggregating properties of the chimeras. Only chimeras with 55Q and 79Q readily form amyloid-like fibrils; therefore, similarly to the proteins associated with diseases, there is a threshold number of glutamines above which the chimeras aggregate into amyloid-like fibrils. Most importantly, the chimera containing 79Q forms amyloid-like fibrils at the same rate whether BlaP is folded or not, whereas the 55Q chimera aggregates into amyloid-like fibrils only if BlaP is unfolded. The threshold value for amyloid-like fibril formation depends, therefore, on the structural integrity of the β-lactamase moiety and thus on the steric and/or conformational constraints applied to the polyQ tract. These constraints have, however, no significant effect on the propensity of the 79Q tract to trigger fibril formation. These results suggest that the influence of the protein context on the aggregating properties of polyQ disease-associated proteins could be negligible when the latter contain particularly long polyQ tracts.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Orr HT, Zoghbi HY. Trinucleotide repeat disorders. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2007;30:575–621. - PubMed
-
- Ordway JM, Tallaksen-Greene S, Gutekunst CA, Bernstein EM, Cearley JA, et al. Ectopically expressed CAG repeats cause intranuclear inclusions and a progressive late onset neurological phenotype in the mouse. Cell. 1997;91:753–763. - PubMed
-
- Zoghbi HY, Orr HT. Glutamine repeats and neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2000;23:217–247. - PubMed
-
- Robertson AL, Bottomley SP. Towards the treatment of polyglutamine diseases: the modulatory role of protein context. Curr Med Chem. 2010;17:3058–3068. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

