Toll-like receptors: key players in antiviral immunity
- PMID: 22440908
- PMCID: PMC3311989
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.006
Toll-like receptors: key players in antiviral immunity
Abstract
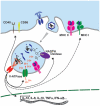
TLRs are a family of innate receptors whose specificities are predetermined in the germline. Therefore, TLRs have evolved to recognize conserved features of microbes. Viruses typically lack the conserved features common to other pathogen classes, so the innate immune system has evolved to recognize viral nucleic acid as a hallmark of viral infection. In this review we discuss examples of TLR-mediated viral recognition and the functional consequences of this recognition for antiviral immunity.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol. 2010;11(5):373–384. - PubMed
-
- Barbalat R, Ewald SE, Mouchess ML, Barton GM. Nucleic acid recognition by the innate immune system. Annual review of immunology. 2011;29:185–214. - PubMed
-
- Stetson DB, Medzhitov R. Type i interferons in host defense. Immunity. 2006;25(3):373–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

