Cytosolic surveillance and antiviral immunity
- PMID: 22440909
- PMCID: PMC3610561
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.11.004
Cytosolic surveillance and antiviral immunity
Abstract
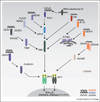
Innate immune surveillance mechanisms lie at the heart of the antiviral response. A growing number of germ-line encoded pattern recognition receptors have been identified which protect the host from infection by sensing the presence of viral molecules and inducing antiviral defenses. Most compartments that viruses gain access to are under active surveillance by one or more pattern recognition receptors. Members of the Toll-like receptor family guard the extracellular milieu and endosomal compartment where they are activated by viral glycoproteins or nucleic acids, respectively. More recently, the cytosolic compartment has emerged as the frontline in the arsenal of the host's antiviral defenses. Families of receptors in the cytosol recognize viral RNA or DNA or perturbations of cellular homeostasis and orchestrate effector responses to eliminate the invader. Here, we review this expanding area of innate immunity by focusing on the molecular mechanisms of cytosolic host-defenses.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Barbalat R, Ewald SE, Mouchess ML, Barton GM. Nucleic acid recognition by the innate immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 2011;29:185–214. - PubMed
-
- Hornung V, Latz E. Intracellular DNA recognition. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:123–130. - PubMed
-
- Fitzgerald KA, McWhirter SM, Faia KL, Rowe DC, Latz E, Golenbock DT, Coyle AJ, Liao SM, Maniatis T. IKKε and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:491–496. - PubMed
-
- Sharma S, tenOever BR, Grandvaux N, Zhou GP, Lin R, Hiscott J. Triggering the interferon antiviral response through an IKK-related pathway. Science. 2003;300:1148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

