Environmental factors affecting the transmission of respiratory viruses
- PMID: 22440971
- PMCID: PMC3311988
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.12.003
Environmental factors affecting the transmission of respiratory viruses
Abstract
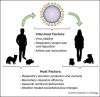
Many viruses are capable of infecting the human respiratory tract to cause disease. These viruses display various transmission patterns among humans; however, they all share the ability to transmit from person to person, and their human transmissibility is influenced by the environment in which pathogen and host meet. This review aims to summarize recent and significant observations regarding the impact of environmental factors such as weather and climate, humidity, temperature, and airflow on the transmission of human respiratory viruses. Where possible, knowledge gaps that require further scientific study will be identified.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Turner R.B. Chapter 53 – the common cold. In: Mandell G.L., Bennett J.E., Dolin R., editors. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. edn 7. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2009. pp. 809–813.
-
- Musher D.M. How contagious are common respiratory tract infections. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1256–1266. - PubMed
-
- Forgie S., Marrie T.J. Healthcare-associated atypical pneumonia. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;30:67–85. - PubMed
-
- Belser J.A., Maines T.R., Tumpey T.M., Katz J.M. Influenza A virus transmission: contributing factors and clinical implications. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2010;12:e39. - PubMed
-
This comprehensive review presents recent progress made in understanding the viral and environmental factors that impact upon efficient person-to-person transmission of influenza virus, as well as the clinical implications of these findings.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

