Disrupting the networks of cancer
- PMID: 22442061
- PMCID: PMC4154593
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0366
Disrupting the networks of cancer
Abstract
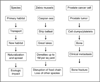
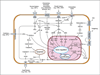
Ecosystems are interactive systems involving communities of species and their abiotic environment. Tumors are ecosystems in which cancer cells act as invasive species interacting with native host cell species in an established microenvironment within the larger host biosphere. At its heart, to study ecology is to study interconnectedness. In ecologic science, an ecologic network is a representation of the biotic interactions in an ecosystem in which species (nodes) are connected by pairwise interactions (links). Ecologic networks and signaling network models have been used to describe and compare the structures of ecosystems. It has been shown that disruption of ecologic networks through the loss of species or disruption of interactions between them can lead to the destruction of the ecosystem. Often, the destruction of a single node or link is not enough to disrupt the entire ecosystem. The more complex the network and its interactions, the more difficult it is to cause the extinction of a species, especially without leveraging other aspects of the ecosystem. Similarly, successful treatment of cancer with a single agent is rarely enough to cure a patient without strategically modifying the support systems conducive to survival of cancer. Cancer cells and the ecologic systems they reside in can be viewed as a series of nested networks. The most effective new paradigms for treatment will be developed through application of scaled network disruption.
©2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
K.J. Pienta is a consultant and is on the advisory board of Curis, Inc. D.F. Camacho disclosed no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Smithers DW. An attack on cytologism. Lancet. 1962;1:493–499. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

