Endocytic trafficking of neurotrophins in neural development
- PMID: 22444728
- PMCID: PMC3348440
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2012.02.005
Endocytic trafficking of neurotrophins in neural development
Abstract
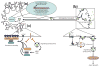
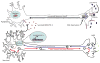
During the formation of neuronal circuits, neurons respond to diffusible cues secreted by target tissues. Often, target-derived signals act on nerve terminals to influence local growth events; in other cases, they are transported long distances back to neuronal cell bodies to effect transcriptional changes necessary for neuronal survival and differentiation. Neurotrophins provide one of the best examples of target-derived cues that elicit an astonishingly diverse array of neuronal responses. Endocytic trafficking of neurotrophins and their receptors is a fundamental feature of neurotrophin signaling, allowing neurotrophins to control neuronal survival by retrograde transport of signaling endosomes containing ligand-receptor complexes. In this review we summarize recent findings that provide new insight into the interplay between neurotrophin signaling and trafficking.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Snider WD. Functions of the Neurotrophins during Nervous System Development: what the knockouts are teaching us. Cell. 1994;77:627–638. - PubMed
-
- Howe CL, Mobley WC. Long-distance retrograde neurotrophic signaling. Current opinion in neurobiology. 2005;15:40–48. - PubMed
-
- Zweifel LS, et al. Functions and mechanisms of retrograde neurotrophin signalling. Nature reviews Neuroscience. 2005;6:615–625. - PubMed
-
- Ye H, et al. Evidence in support of signaling endosome-based retrograde survival of sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 2003;39:57–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

