HIF1α induced switch from bivalent to exclusively glycolytic metabolism during ESC-to-EpiSC/hESC transition
- PMID: 22446391
- PMCID: PMC3343469
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.71
HIF1α induced switch from bivalent to exclusively glycolytic metabolism during ESC-to-EpiSC/hESC transition
Abstract
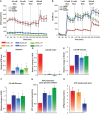
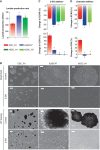
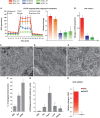
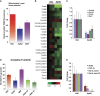
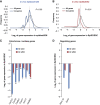
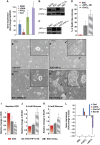
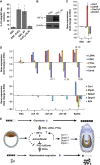
The function of metabolic state in stemness is poorly understood. Mouse embryonic stem cells (ESC) and epiblast stem cells (EpiSC) are at distinct pluripotent states representing the inner cell mass (ICM) and epiblast embryos. Human embryonic stem cells (hESC) are similar to EpiSC stage. We now show a dramatic metabolic difference between these two stages. EpiSC/hESC are highly glycolytic, while ESC are bivalent in their energy production, dynamically switching from glycolysis to mitochondrial respiration on demand. Despite having a more developed and expanding mitochondrial content, EpiSC/hESC have low mitochondrial respiratory capacity due to low cytochrome c oxidase (COX) expression. Similarly, in vivo epiblasts suppress COX levels. These data reveal EpiSC/hESC functional similarity to the glycolytic phenotype in cancer (Warburg effect). We further show that hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α) is sufficient to drive ESC to a glycolytic Activin/Nodal-dependent EpiSC-like stage. This metabolic switch during early stem-cell development may be deterministic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bendall SC, Stewart MH, Menendez P, George D, Vijayaragavan K, Werbowetski-Ogilvie T, Ramos-Mejia V, Rouleau A, Yang J, Bosse M, Lajoie G, Bhatia M (2007) IGF and FGF cooperatively establish the regulatory stem cell niche of pluripotent human cells in vitro. Nature 448: 1015–1021 - PubMed
-
- Bertoni-Freddari C, Fattoretti P, Giorgetti B, Solazzi M, Balietti M, Casoli T, Di Stefano G (2004) Cytochrome oxidase activity in hippocampal synaptic mitochondria during aging: a quantitative cytochemical investigation. Ann NY Acad Sci 1019: 33–36 - PubMed
-
- Brons IG, Smithers LE, Trotter MW, Rugg-Gunn P, Sun B, Chuva de Sousa Lopes SM, Howlett SK, Clarkson A, Ahrlund-Richter L, Pedersen RA, Vallier L (2007) Derivation of pluripotent epiblast stem cells from mammalian embryos. Nature 448: 191–195 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

