Health status and risk indicator trends of the aging US health care workforce
- PMID: 22446575
- PMCID: PMC3323772
- DOI: 10.1097/JOM.0b013e318247a379
Health status and risk indicator trends of the aging US health care workforce
Abstract
Objectives: To describe the health status and risk indicator trends in a representative sample of US health care workers aged 45 years and older.
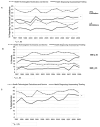
Methods: Using pooled data from the 1997 to 2009 National Health Interview Survey, logistic regression analyses were performed to determine whether age-group specific morbidity risks differed within occupational subgroups of the health care workforce (N = 6509). Health and morbidity trends were examined via complex survey adjusted and weighted chi-squared tests.
Results: Rates of functional limitation and hypertension increased among diagnosing/assessing health care workers. The prevalence of hearing impairment, cancer, and hypertension was two to three times greater in health-diagnosing/assessing workers aged 60 years and older than in younger workers. Health care service workers were up to 19 times more likely to be obese than workers who diagnose/assess health.
Conclusions: Healthier workplaces and targeted interventions are needed to optimize the ability to meet health care demands of this aging workforce.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared
Figures
References
-
- Wegman DH. Older workers. Occup Med. 1999 Jul-Sep;14(3):537–557. - PubMed
-
- Wegman DH, McGee JP. Health and Safety Needs of Older Workers. Washington, D.C: The National Academies Press; 2004. - PubMed
-
- BLS. [Accessed November 10, 2011];Occupational outlook handbook. (2011). 2010–2011 http://www.bls.gov/oco/oco2003.htm.
-
- IOM. Retooling for an aging America: Building the health care workforce. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 2008. - PubMed
-
- Fleming LE, Lee DJ, Martinez AJ, et al. The health behaviors of the older US worker. Am J Ind Med. 2007 Jun;50(6):427–437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources