Mutations in CIZ1 cause adult onset primary cervical dystonia
- PMID: 22447717
- PMCID: PMC3334472
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.23547
Mutations in CIZ1 cause adult onset primary cervical dystonia
Abstract
Objective: Primary dystonia is usually of adult onset, can be familial, and frequently involves the cervical musculature. Our goal was to identify the causal mutation in a family with adult onset, primary cervical dystonia.
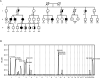
Methods: Linkage and haplotype analyses were combined with solution-based whole-exome capture and massively parallel sequencing in a large Caucasian pedigree with adult onset, primary cervical dystonia to identify a cosegregating mutation. High-throughput screening and Sanger sequencing were completed in 308 Caucasians with familial or sporadic adult onset cervical dystonia and matching controls for sequence variants in this mutant gene.
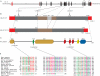
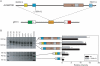
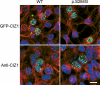
Results: Exome sequencing led to the identification of an exonic splicing enhancer mutation in exon 7 of CIZ1 (c.790A>G, p.S264G), which encodes CIZ1, Cip1-interacting zinc finger protein 1. CIZ1 is a p21(Cip1/Waf1) -interacting zinc finger protein expressed in brain and involved in DNA synthesis and cell-cycle control. Using a minigene assay, we showed that c.790A>G altered CIZ1 splicing patterns. The p.S264G mutation also altered the nuclear localization of CIZ1. Screening in subjects with adult-onset cervical dystonia identified 2 additional CIZ1 missense mutations (p.P47S and p.R672M).
Interpretation: Mutations in CIZ1 may cause adult onset, primary cervical dystonia, possibly by precipitating neurodevelopmental abnormalities that manifest in adults and/or G1/S cell-cycle dysregulation in the mature central nervous system.
Copyright © 2012 American Neurological Association.
Figures
References
-
- Defazio G, Abbruzzese G, Livrea P, Berardelli A. Epidemiology of primary dystonia. Lancet Neurol. 2004;3:673–678. - PubMed
-
- Duane DD. Familial cervical dystonia, head tremor, and scoliosis: a case report. Adv Neurol. 1998;78:117–120. - PubMed
-
- Chan J, Brin MF, Fahn S. Idiopathic cervical dystonia: clinical characteristics. Mov Disord. 1991;6:119–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS057567/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50NS072187/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS082296/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS067501/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54NS065701/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 TR001456/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 NS070276/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS065701/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS048458/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025008/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS048458/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1RC2NS070276/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057567/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30NS05710/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS069936/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS069936/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS072187/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

