MicroRNAs in heart development
- PMID: 22449848
- PMCID: PMC4888772
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387786-4.00009-9
MicroRNAs in heart development
Abstract
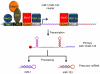
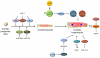
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small noncoding RNAs of ~22nt in length which are involved in the regulation of gene expression at the posttranscriptional level by degrading their target mRNAs and/or inhibiting their translation. Expressed ubiquitously or in a tissue-specific manner, miRNAs are involved in the regulation of many biological processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and the maintenance of normal cellular physiology. Many miRNAs are expressed in embryonic, postnatal, and adult hearts. Aberrant expression or genetic deletion of miRNAs is associated with abnormal cardiac cell differentiation, disruption of heart development, and cardiac dysfunction. This chapter will summarize the history, biogenesis, and processing of miRNAs as well as their function in heart development, remodeling, and disease.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Alberts B, Bray D, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Watson J. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 3rd. Garland publishing; New York & London: 1994. pp. 72–73. 292–334.
-
- Ambros V, Horvitz HR. Heterochronic mutants of the Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 1984;226:409–416. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V, Horvitz HR. The lin-14 locus of Caenorhabditis elegans controls the time of expression of specific postembryonic developmental events. Genes Dev. 1987;1:398–414. - PubMed
-
- Anderson P. Mutagenesis. In: Epstein F, Shakes C, editors. Caenorhabditis elegans: Modern Biological Analysis of an Organism. Academic press; California: 1995. pp. 31–54.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

