Diagnostic challenges in chronic antibody-mediated rejection
- PMID: 22450441
- PMCID: PMC3726203
- DOI: 10.1038/nrneph.2012.61
Diagnostic challenges in chronic antibody-mediated rejection
Abstract
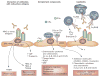
Measurement of glomerular and peritubular capillaritis in kidney transplant biopsy samples identifies allograft dysfunction associated with alloantibodies. Sis et al. show that this technique has a higher sensitivity but lower specificity than the current diagnostic criteria using peritubular capillary C4d deposition, and that capillaritis is an independent predictor of progression to graft failure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gaston RS, et al. Evidence for antibody-mediated injury as a major determinant of late kidney allograft failure. Transplantation. 2010;90:68–74. - PubMed
-
- Solez K, et al. Banff ‘05 Meeting Report: differential diagnosis of chronic allograft injury and elimination of chronic allograft nephropathy (‘CAN’) Am J Transplant. 2007;7:518–526. - PubMed
-
- Regele H, et al. Capillary deposition of complement split product C4d in renal allografts is associated with basement membrane injury in peritubular and glomerular capillaries: a contribution of humoral immunity to chronic allograft rejection. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:2371–2380. - PubMed
-
- Gibson IW, et al. Peritubular capillaritis in renal allografts: prevalence, scoring system, reproducibility and clinicopathological correlates. Am J Transplant. 2008;8:819–825. - PubMed
-
- Loupy A, et al. Significance of C4d Banff scores in early protocol biopsies of kidney transplant recipients with preformed donor-specific antibodies (DSA) Am J Transplant. 2011;11:56–65. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

