Mood response to deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 22450611
- PMCID: PMC3354989
- DOI: 10.1176/appi.neuropsych.11030060
Mood response to deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
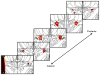
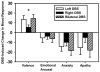
Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus (STN DBS) in Parkinson's disease (PD) improves motor functioning but has variable effects on mood. Little is known about the relationship between electrode contact location and mood response. The authors identified the anatomical location of electrode contacts and measured mood response to stimulation with the Visual Analog Scale in 24 STN DBS PD patients. Participants reported greater positive mood and decreased anxiety and apathy with bilateral and unilateral stimulation. Left DBS improved mood more than right DBS. Right DBS-induced increase in positive mood was related to more medial and dorsal contact locations. These results highlight the functional heterogeneity of the STN.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Karimi previously received partial fellowship funding from Medtronic, Inc., the manufacturer of the implanted stimulators; no other authors have any conflicts of interest related to this research.
Figures
References
-
- Limousin P, Pollak P, Benazzouz A, Hoffmann D, Broussolle E, Perret JE, Benabid AL. Bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation for severe Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 1995;10:672–4. - PubMed
-
- Temel Y, Kessels A, Tan S, Topdag A, Boon P, Visser-Vandewalle V. Behavioural changes after bilateral subthalamic stimulation in advanced Parkinson disease: a systematic review. Parkinsonism. Relat Disord. 2006;12:265–72. - PubMed
-
- Burn DJ, Troster AI. Neuropsychiatric complications of medical and surgical therapies for Parkinson’s disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2004;17:172–80. - PubMed
-
- Troster AI. Neuropsychology of deep brain stimulation in neurology and psychiatry. Front Biosci. 2009;14:1857–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

