2011 Rita Schaffer lecture: nanoparticles for intracellular nucleic acid delivery
- PMID: 22451256
- PMCID: PMC3380081
- DOI: 10.1007/s10439-012-0550-3
2011 Rita Schaffer lecture: nanoparticles for intracellular nucleic acid delivery
Abstract
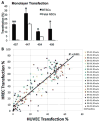
Nanoparticles are a promising technology for delivery of new types of therapeutics. A polymer library approach has allowed engineering of polymeric particles that are particularly effective for the delivery of DNA and siRNA to human cells. Certain chemical structural motifs, degradable linkages, hydrophobicity, and biophysical properties are key for successful intracellular delivery. Small differences to biomaterial structure, and especially the type of degradable linkage in the polymers, can be critical for successful delivery of siRNA vs. DNA. Furthermore, subtle changes to biomaterial structure can facilitate cell-type gene delivery specificity between human brain cancer cells and healthy cells as well as between human retinal endothelial cells and epithelial cells. These polymeric nanoparticles are effective for nucleic acid delivery in a broad range of human cell types and have applications to regenerative medicine, ophthalmology, and cancer among many other biomedical research areas.
Figures


References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts and figures. 2005. Cancer facts and figures 2012: American Cancer Society.
-
- Gene therapy clinical trials worldwide. J Gene Medicine. 2012
-
- Acharya S, Sahoo SK. PLGA nanoparticles containing various anticancer agents and tumour delivery by EPR effect. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2011;63(3):170–183. - PubMed
-
- Anderson DG, Lynn DM, Langer R. Semi-automated synthesis and screening of a large library of degradable cationic polymers for gene delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2003;42:3153–3158. - PubMed
-
- Arote RB, Jiang HL, Kim YK, Cho MH, Choi YJ, Cho CS. Degradable poly(amido amine)s as gene delivery carriers. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2011;8(9):1237–1246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

