Evaluation of resveratrol, green tea extract, curcumin, oxaloacetic acid, and medium-chain triglyceride oil on life span of genetically heterogeneous mice
- PMID: 22451473
- PMCID: PMC3598361
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/gls070
Evaluation of resveratrol, green tea extract, curcumin, oxaloacetic acid, and medium-chain triglyceride oil on life span of genetically heterogeneous mice
Abstract
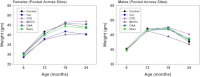
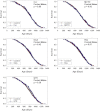
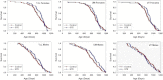
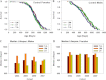
The National Institute on Aging Interventions Testing Program (ITP) was established to evaluate agents that are hypothesized to increase life span and/or health span in genetically heterogeneous mice. Each compound is tested in parallel at three test sites. It is the goal of the ITP to publish all results, negative or positive. We report here on the results of lifelong treatment of mice, beginning at 4 months of age, with each of five agents, that is, green tea extract (GTE), curcumin, oxaloacetic acid, medium-chain triglyceride oil, and resveratrol, on the life span of genetically heterogeneous mice. Each agent was administered beginning at 4 months of age. None of these five agents had a statistically significant effect on life span of male or female mice, by log-rank test, at the concentrations tested, although a secondary analysis suggested that GTE might diminish the risk of midlife deaths in females only.
Figures


References
-
- Olshansky SJ, Carnes BA, Cassel C. In search of Methuselah: estimating the upper limits to human longevity. Science. 1990;250(4981):634–640. - PubMed
-
- Olshansky SJ. Commentary: prescient visions of public health from Cornaro to Breslow. Int J Epidemiol. 2006;35(1):22–23. - PubMed
-
- Archer JR, Harrison DE. L-Deprenyl treatment in aged mice slightly increases life spans, and greatly reduces fecundity by aged males. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1996;51(6):B448–B453. - PubMed
-
- Schneider EL, Reed JD., Jr Life extension. N Engl J Med. 1985;312(18):1159–1168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 AG038070/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG13925/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG013925/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG028730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG022308/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG013925/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG025707/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG022303/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG024824/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY007042/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG022303/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AG13319/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019719/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG022307/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

