Primary squamous cell carcinoma of thyroid: a case report and review of literature
- PMID: 22452749
- PMCID: PMC3331844
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-3284-4-8
Primary squamous cell carcinoma of thyroid: a case report and review of literature
Expression of concern in
-
Comment: Head and Neck Oncology.BMC Med. 2014 Feb 5;12:24. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-12-24. BMC Med. 2014. PMID: 24499430 Free PMC article. Review.
Abstract
Background: Thyroid gland lacks squamous epithelium (except in some rare situations like embroyonic remnants or in inflammatory processes); for that reason the primary squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of thyroid is extremely rare entity, seen only in less than 1% of all thyroid malignancies and is considered almost fatal. So, far, only few case reports have been published in literature.
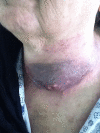
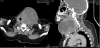
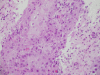
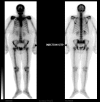
Case presentation: Herein we present a 54 years old Saudi female with 3 months history of progressive neck swelling and hoarse voice, who was referred to us by her primary care physician as suspected case of anaplastic carcinoma of thyroid for radical external beam radiation therapy (EBRT). Fine Needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) revealed squamous cell carcinoma. Computed tomography (CT) neck showed 10 × 10 cm mass in left lobe of thyroid invading trachea and skin. Extensive staging work up ruled out the possibility of any primary site of SCC other than thyroid gland. Tumor was found unresectable and was referred to radiation oncology. She received palliative EBRT 30 Gy in 10 fractions. After completion of EBRT, there was progression of disease and patient died 3 months after completion of EBRT by airway compromise.
Conclusion: Primary SCC of thyroid is rare and aggressive entity. FNAC is reliable and effective tool for immediate diagnosis. Surgery is a curative option, but it is not always possible as most of cases present as locally advanced with adjacent organs involvement. EBRT alone was found ineffective. Aggressive combined modality (debulking surgery, radiation and chemotherapy) shall be considered for such cases.
© 2012 Tunio et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

