Trophic factors and cell therapy to stimulate brain repair after ischaemic stroke
- PMID: 22452968
- PMCID: PMC3823421
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2012.01575.x
Trophic factors and cell therapy to stimulate brain repair after ischaemic stroke
Abstract
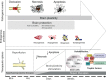
Brain repair involves a compendium of natural mechanisms that are activated following stroke. From a therapeutic viewpoint, reparative therapies that encourage cerebral plasticity are needed. In the last years, it has been demonstrated that modulatory treatments for brain repair such as trophic factor- and stem cell-based therapies can promote neurogenesis, gliogenesis, oligodendrogenesis, synaptogenesis and angiogenesis, all of which having a beneficial impact on infarct volume, cell death and, finally, and most importantly, on the functional recovery. However, even when promising results have been obtained in a wide range of experimental animal models and conditions these preliminary results have not yet demonstrated their clinical efficacy. Here, we focus on brain repair modulatory treatments for ischaemic stroke, that use trophic factors, drugs with trophic effects and stem cell therapy. Important and still unanswered questions for translational research ranging from experimental animal models to recent and ongoing clinical trials are reviewed here.
© 2012 The Authors Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine © 2012 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Cramer SC. Repairing the human brain after stroke: I. Mechanisms of spontaneous recovery. Ann Neurol. 2008;63:272–87. - PubMed
-
- Cramer SC. Repairing the human brain after stroke. II. Restorative therapies. Ann Neurol. 2008;63:549–60. - PubMed
-
- Lo EH. A new penumbra: transitioning from injury into repair after stroke. Nat Med. 2008;14:497–500. - PubMed
-
- Alonso de Leciñana M, Díez-Tejedor E, Gutiérrez M, et al. New goals in ischemic stroke therapy: the experimental approach-harmonizing science with practice. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2005;20:159–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

