Ameliorative effect of supplementation with L-glutamine on oxidative stress, DNA damage, cell viability and hepatotoxicity induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in rat hepatocyte cultures
- PMID: 22453904
- PMCID: PMC3488374
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-012-9449-y
Ameliorative effect of supplementation with L-glutamine on oxidative stress, DNA damage, cell viability and hepatotoxicity induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in rat hepatocyte cultures
Abstract
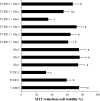
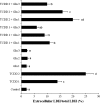
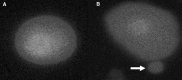
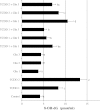
The most potent of the dioxins, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), is a persistent and ubiquitous environmental contaminant. And the health impact of exposure to TCDD is of great concern to the general public. Recent data indicate that L-glutamine (Gln) has antioxidant properties and may influence hepatotoxicity. The objective of the present study was undertaken to explore the effectiveness of Gln in alleviating the hepatotoxicity of TCDD on primary cultured rat hepatocytes. Gln (0.5, 1 and 2 mM) was added to cultures alone or simultaneously with TCDD (0.005 and 0.01 mM). The hepatocytes were treated with TCDD and Gln for 48 h. Then cell viability was detected by [3-(4,5-dimethyl-thiazol-2-yl) 2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] (MTT) assay and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release, while total antioxidant capacity (TAC), total glutathione (TGSH) and total oxidative stress (TOS) levels were determined to evaluate the oxidative injury. The DNA damage was also analyzed by liver micronucleus assay (MN) and 8-oxo-2-deoxyguanosine (8-OH-dG). The results of MTT and LDH assays showed that TCDD decreased cell viability but not L-glutamine. TCDD also increased TOS level in rat hepatocytes and significantly decreased TAC and TGSH levels. On the basis of increasing doses, the dioxin in a dose-dependent manner caused significant increases of micronucleated hepatocytes (MNHEPs) and 8-OH-dG as compared to control culture. Whereas, in cultures exposured with Gln alone, TOS levels were not changed and TAC and TGSH together were significantly increased in dose-dependent fashion. The presence of Gln with TCDD modulated the hepatotoxic effects of TCDD on primary hepatocytes cultures. Noteworthy, Gln has a protective effect against TCDD-mediated DNA damages. As conclusion, we reported here an increased potential therapeutic significance of L-glutamine in TCDD-mediated hepatic injury for the first time.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

