The FF4 and FF5 domains of transcription elongation regulator 1 (TCERG1) target proteins to the periphery of speckles
- PMID: 22453921
- PMCID: PMC3366829
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.304782
The FF4 and FF5 domains of transcription elongation regulator 1 (TCERG1) target proteins to the periphery of speckles
Abstract
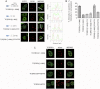
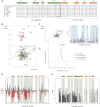
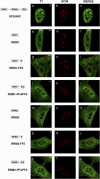
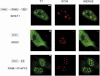
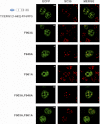
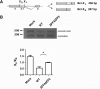
Transcription elongation regulator 1 (TCERG1) is a human factor implicated in interactions with the spliceosome as a coupler of transcription and splicing. The protein is highly concentrated at the interface between speckles (the compartments enriched in splicing factors) and nearby transcription sites. Here, we identified the FF4 and FF5 domains of TCERG1 as the amino acid sequences required to direct this protein to the periphery of nuclear speckles, where coordinated transcription/RNA processing events occur. Consistent with our localization data, we observed that the FF4 and FF5 pair is required to fold in solution, thus suggesting that the pair forms a functional unit. When added to heterologous proteins, the FF4-FF5 pair is capable of targeting the resulting fusion protein to speckles. This represents, to our knowledge, the first description of a targeting signal for the localization of proteins to sites peripheral to speckled domains. Moreover, this "speckle periphery-targeting signal" contributes to the regulation of alternative splicing decisions of a reporter pre-mRNA in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Specific interaction of the transcription elongation regulator TCERG1 with RNA polymerase II requires simultaneous phosphorylation at Ser2, Ser5, and Ser7 within the carboxyl-terminal domain repeat.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 12;288(15):10890-901. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.460238. Epub 2013 Feb 22. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23436654 Free PMC article.
-
TCERG1 regulates alternative splicing of the Bcl-x gene by modulating the rate of RNA polymerase II transcription.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Feb;32(4):751-62. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06255-11. Epub 2011 Dec 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22158966 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the cellular targets of the transcription factor TCERG1 reveals a prevalent role in mRNA processing.J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 21;283(12):7949-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709402200. Epub 2008 Jan 10. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18187414
-
Emerging and re-emerging themes in co-transcriptional pre-mRNA splicing.Mol Cell. 2024 Oct 3;84(19):3656-3666. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.08.036. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 39366353 Review.
-
Coupling of RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation with Pre-mRNA Splicing.J Mol Biol. 2016 Jun 19;428(12):2623-2635. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.04.017. Epub 2016 Apr 20. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27107644 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prp40 pre-mRNA processing factor 40 homolog B (PRPF40B) associates with SF1 and U2AF65 and modulates alternative pre-mRNA splicing in vivo.RNA. 2015 Mar;21(3):438-57. doi: 10.1261/rna.047258.114. Epub 2015 Jan 20. RNA. 2015. PMID: 25605964 Free PMC article.
-
The in vivo dynamics of TCERG1, a factor that couples transcriptional elongation with splicing.RNA. 2016 Apr;22(4):571-82. doi: 10.1261/rna.052795.115. Epub 2016 Feb 12. RNA. 2016. PMID: 26873599 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of TCERG1 as a new genetic modulator of TDP-43 production in Drosophila.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2018 Dec 12;6(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s40478-018-0639-5. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2018. PMID: 30541625 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of the Early Spliceosomal Complex-From Constitutive to Regulated Splicing.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 18;22(22):12444. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212444. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA recognition and self-association of CPEB4 is mediated by its tandem RRM domains.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Sep;42(15):10185-95. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku700. Epub 2014 Jul 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25081215 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

