Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus vIRF-3 protein binds to F-box of Skp2 protein and acts as a regulator of c-Myc protein function and stability
- PMID: 22453922
- PMCID: PMC3351320
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.335216
Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus vIRF-3 protein binds to F-box of Skp2 protein and acts as a regulator of c-Myc protein function and stability
Abstract
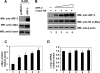
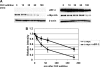
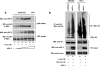
The Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) has been linked to Kaposi sarcoma, body cavity-based lymphoma, and Castleman disease. vIRF-3 is a KSHV latent gene that is critical for proliferation of KSHV-positive lymphoid cells. Furthermore, vIRF-3 contributes to KSHV-associated pathogenesis by stimulating c-Myc transcription activity. Here we show that vIRF-3 can associate with Skp2, a key component of the SCF(skp2) ubiquitin ligase complex. Skp2 is a transcriptional co-factor for c-Myc that was shown to regulate the stability of c-Myc protein as well as c-Myc-dependent transcription. In this study, we show that vIRF-3 binds to the F-box of Skp2 and recruits it to c-Myc-regulated promoters to activate c-Myc-dependent transcription. Additionally, cells overexpressing vIRF-3 exhibit higher levels of c-Myc ubiquitylation, suggesting that ubiquitylation is necessary for c-Myc-mediated transcription. Moreover, vIRF-3 can stabilize the c-Myc protein by increasing its half-life. Collectively, these results indicate that vIRF-3 can effectively manipulate c-Myc stability and function and thus contribute to c-Myc-induced KSHV-associated lymphomagenesis.
Figures


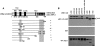

References
-
- Cesarman E., Chang Y., Moore P. S., Said J. W., Knowles D. M. (1995) Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 332, 1186–1191 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

