Potential biological functions of cytochrome P450 reductase-dependent enzymes in small intestine: novel link to expression of major histocompatibility complex class II genes
- PMID: 22453923
- PMCID: PMC3366852
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.354274
Potential biological functions of cytochrome P450 reductase-dependent enzymes in small intestine: novel link to expression of major histocompatibility complex class II genes
Abstract
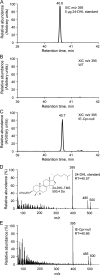
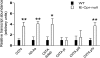
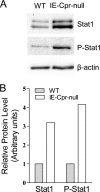
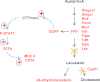
NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase (POR) is essential for the functioning of microsomal cytochrome P450 (P450) monooxygenases and heme oxygenases. The biological roles of the POR-dependent enzymes in the intestine have not been defined, despite the wealth of knowledge on the biochemical properties of the various oxygenases. In this study, cDNA microarray analysis revealed significant changes in gene expression in enterocytes isolated from the small intestine of intestinal epithelium-specific Por knock-out (named IE-Cpr-null) mice compared with that observed in wild-type (WT) littermates. Gene ontology analyses revealed significant changes in terms related to P450s, transporters, cholesterol biosynthesis, and, unexpectedly, antigen presentation/processing. The genomic changes were confirmed at either mRNA or protein level for selected genes, including those of the major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC II). Cholesterol biosynthetic activity was greatly reduced in the enterocytes of the IE-Cpr-null mice, as evidenced by the accumulation of the lanosterol metabolite, 24-dihydrolanosterol. However, no differences in either circulating or enterocyte cholesterol levels were observed between IE-Cpr-null and WT mice. Interestingly, the levels of the cholesterol precursor farnesyl pyrophosphate and its derivative geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate were also increased in the enterocytes of the IE-Cpr-null mice. Furthermore, the expression of STAT1 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 1), a downstream target of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate signaling, was enhanced. STAT1 is an activator of CIITA, the class II transactivator for MHC II expression; CIITA expression was concomitantly increased in IE-Cpr-null mice. Overall, these findings provide a novel and mechanistic link between POR-dependent enzymes and the expression of MHC II genes in the small intestine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An intestinal epithelium-specific cytochrome P450 (P450) reductase-knockout mouse model: direct evidence for a role of intestinal p450s in first-pass clearance of oral nifedipine.Drug Metab Dispos. 2009 Mar;37(3):651-7. doi: 10.1124/dmd.108.025429. Epub 2008 Dec 4. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009. PMID: 19056912 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic gene expression changes in mouse models with liver-specific deletion or global suppression of the NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase gene. Mechanistic implications for the regulation of microsomal cytochrome P450 and the fatty liver phenotype.J Biol Chem. 2005 Sep 9;280(36):31686-98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M504447200. Epub 2005 Jul 8. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16006652
-
Intestinal epithelium-specific knockout of the cytochrome P450 reductase gene exacerbates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015 Jul;354(1):10-7. doi: 10.1124/jpet.115.223263. Epub 2015 Apr 29. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015. PMID: 25926522 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of MHC II genes.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;290:147-70. doi: 10.1007/3-540-26363-2_7. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16480042 Review.
-
Mini-review: Specificity and expression of CIITA, the master regulator of MHC class II genes.Eur J Immunol. 2004 Jun;34(6):1513-25. doi: 10.1002/eji.200424964. Eur J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15162420 Review.
Cited by
-
NADPH-cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase: roles in physiology, pharmacology, and toxicology.Drug Metab Dispos. 2013 Jan;41(1):12-23. doi: 10.1124/dmd.112.048991. Epub 2012 Oct 19. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013. PMID: 23086197 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Functionally Segmented Intestine in Tunicate Ascidian.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 27;24(7):6270. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076270. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047242 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of P450-mediated vitamin E hydroxylase activities alters vitamin E status in tocopherol supplemented mice and reveals extra-hepatic vitamin E metabolism.J Lipid Res. 2012 Dec;53(12):2667-76. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M030734. Epub 2012 Sep 11. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22969154 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of Dietary Protein and Prebiotic Inclusion on Liver and Spleen Gene Expression in Hy-Line Brown Caged Layers.Animals (Basel). 2020 Mar 9;10(3):453. doi: 10.3390/ani10030453. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32182781 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic and intestinal biotransformation gene expression and drug disposition in a dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mouse model.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 Jan;10(1):123-135. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.12.002. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 31993311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taniguchi H., Imai Y., Sato R. (1984) Role of electron transfer system in microsomal drug monooxygenase reaction catalyzed by cytochrome P450. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 232, 585–596 - PubMed
-
- Schacter B.A., Nelson E. B., Marver H. S., Masters B. S. (1972) Immunochemical evidence for an association of heme oxygenase with the microsomal electron transport system. J. Biol. Chem. 247, 3601–3607 - PubMed
-
- Ono T., Bloch K. (1975) Solubilization and partial characterization of rat liver squalene epoxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 250, 1571–1579 - PubMed
-
- Shen A. L., O'Leary K. A., Kasper C. B. (2002) Association of multiple developmental defects and embryonic lethality with loss of microsomal NADPH-cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 6536–6541 - PubMed
-
- Flück C. E., Tajima T., Pandey A. V., Arlt W., Okuhara K., Verge C. F., Jabs E. W., Mendonça B. B., Fujieda K., Miller W. L. (2004) Mutant P450 oxidoreductase causes disordered steroidogenesis with and without Antley-Bixler syndrome. Nat. Genet. 36, 228–230 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

