Stem cells and calcium signaling
- PMID: 22453975
- PMCID: PMC3979962
- DOI: 10.1007/978-94-007-2888-2_40
Stem cells and calcium signaling
Abstract
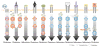
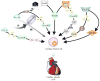
The increasing interest in stem cell research is linked to the promise of developing treatments for many lifethreatening, debilitating diseases, and for cell replacement therapies. However, performing these therapeutic innovations with safety will only be possible when an accurate knowledge about the molecular signals that promote the desired cell fate is reached. Among these signals are transient changes in intracellular Ca(2+) concentration [Ca(2+)](i). Acting as an intracellular messenger, Ca(2+) has a key role in cell signaling pathways in various differentiation stages of stem cells. The aim of this chapter is to present a broad overview of various moments in which Ca(2+)-mediated signaling is essential for the maintenance of stem cells and for promoting their development and differentiation, also focusing on their therapeutic potential.
Figures

References
-
- Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000;1:11–21. - PubMed
-
- Kawano S, Shoji S, Ichinose S, Yamagata K, Tagami M, Hiraoka M. Characterization of Ca(2+) signaling pathways in human mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Calcium. 2002;32:165–174. - PubMed
-
- Kawano S, Otsu K, Shoji S, Yamagata K, Hiraoka M. Ca(2+) oscillations regulated by Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger and plasma membrane Ca(2+) pump induce fluctuations of membrane currents and potentials in human mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Calcium. 2003;34:145–156. - PubMed
-
- Li GR, Sun H, Deng X, Lau CP. Characterization of ionic currents in human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow. Stem Cells. 2005;23:371–382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

