Traditional chinese herbal patch for short-term management of knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 22454655
- PMCID: PMC3292236
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/171706
Traditional chinese herbal patch for short-term management of knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
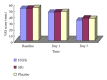
Objective. To assess the short-term efficacy and safety of two kinds of Traditional Chinese herbal patches, Fufang Nanxing Zhitong Gao (FNZG) and Shangshi Jietong Gao (SJG), for painful knee osteoarthritis (OA). Methods. Patients were randomly enrolled in a double-blind, placebo-controlled study to receive FNZG (n = 60), SJG (n = 60), or placebo patch (n = 30) for 7 days. Outcome measures included visual analogue scale (VAS), Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC), and Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome Questionnaire (TCMSQ) subscale. Results. Although there was no significant difference among, three groups in short-term pain management, patients receiving FNZG got significant improvement in symptom of fear of coldness as compared with placebo patch (P = 0.029). The most common local adverse events of rash, itching, erythema, and slightly damaged skin were observed in 7% of participants. Conclusions. FNZG may be a useful treatment for symptom of knee OA and merits long-term study in broader populations.
Figures
References
-
- Felson DT. Osteoarthritis of the knee. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2006;354(8):841–848. - PubMed
-
- Zhang W, Nuki G, Moskowitz RW, et al. OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis. Part III: changes in evidence following systematic cumulative update of research published through January 2009. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 2010;18(4):476–499. - PubMed
-
- Qiu G. Osteoarthritis diagnosis and treatment guidelines. Chinese of Journal Joint Surgery. 2007;1(4):281–285. (electronic edition)
-
- China State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Clinical Path of Traditional Chinese Medicine 22 Professional 95 Diseases. Beijing, China: China Traditional Chinese Medicine Press; 2011.
-
- Deng ZJ. Formula Study. Beijing, China: China Traditional Chinese Medicine Press; 2005.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources