Intravitreal triamcinolone for acute branch retinal vein occlusion: a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 22454718
- PMCID: PMC3306087
Intravitreal triamcinolone for acute branch retinal vein occlusion: a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the therapeutic effect of intravitreal triamcinolone (IVT) injection for recent branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO).
Methods: In a randomized controlled clinical trial, 30 phakic eyes with recent (less than 10 weeks' duration) BRVO were assigned to two groups. The treatment group (16 eyes) received 4 mg IVT and the control group (14 eyes) received subconjunctival sham injections. Changes in visual acuity (VA) were the main outcome measure.
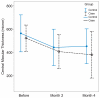
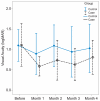
Results: VA and central macular thickness (CMT) changes were not significantly different between the study groups at any time point. Within group analysis showed significant VA improvement from baseline in the IVT group up to three months (P < 0.05); the amount of this change was -0.53 ± 0.46, -0.37 ± 0.50, -0.46 ± 0.50, and -0.29 ± 0.45 logMAR at 1, 2, 3, and 4 months, respectively. Corresponding VA improvements in the control group were -0.20 ± 0.37, -0.11 ± 0.46, -0.25 ± 0.58, and -0.05 ± 0.50 logMAR (all P values > 0.05). Significant reduction in CMT was noticed only in the treatment group (-172 ± 202 μm, P = 0.029) and at 4 months. Ocular hypertension occurred in 4 (25%) and 2 (14.3%) eyes in the IVT and control groups, respectively.
Conclusion: A single IVT injection had a non-significant beneficial effect on VA and CMT in acute BRVO as compared to the natural history of the condition. The 3-month deferred treatment protocol advocated by the Branch Vein Occlusion Study Group may be a safer option than IVT injection considering its potential side effects.
Keywords: Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion; Central Macular Thickness; Intraocular Pressure; Intravitreal Triamcinolone; Macular Edema; Neovascularization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Three intravitreal bevacizumab versus two intravitreal triamcinolone injections in recent-onset branch retinal vein occlusion.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012 Aug;250(8):1149-60. doi: 10.1007/s00417-012-1941-8. Epub 2012 Feb 14. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012. PMID: 22331147 Clinical Trial.
-
Prospective study of intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide versus bevacizumab for macular edema secondary to central retinal vein occlusion.Retina. 2011 May;31(5):838-45. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e3181f4420d. Retina. 2011. PMID: 21293319 Clinical Trial.
-
Three intravitreal bevacizumab versus two intravitreal triamcinolone injections in recent onset central retinal vein occlusion.Acta Ophthalmol. 2014 Nov;92(7):e530-9. doi: 10.1111/aos.12317. Epub 2013 Dec 26. Acta Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 24373344 Clinical Trial.
-
Intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide for treatment of intraocular oedematous and neovascular diseases.Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2005 Dec;83(6):645-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0420.2005.00592.x. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2005. PMID: 16396641 Review.
-
Steroids and macular edema from retinal vein occlusion.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2011;21 Suppl 6:S37-44. doi: 10.5301/EJO.2010.6053. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 23264327 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural Short-term Course of Recurrent Macular Edema Following Intravitreal Bevacizumab Therapy in Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion.Korean J Ophthalmol. 2017 Apr;31(2):95-101. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2017.31.2.95. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28367036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mitchell P, Smith W, Chang A. Prevalence and associations of retinal vein occlusion in Australia. The Blue Mountains Eye Study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996;114:1243–1247. - PubMed
-
- The Branch Vein Occlusion Study Group. Argon laser photocoagulation for macular edema in branch vein occlusion. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984;98:271–282. - PubMed
-
- Lin JM, Chiu YT, Hung PT, Tsai YY. Early treatment of severe cystoid macular edema in central retinal vein occlusion with posterior subtenon triamcinolone acetonide. Retina. 2007;27:180–189. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources