Inflammation modulates human HDL composition and function in vivo
- PMID: 22456230
- PMCID: PMC3361641
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.02.032
Inflammation modulates human HDL composition and function in vivo
Abstract
Objectives: Inflammation may directly impair HDL functions, in particular reverse cholesterol transport (RCT), but limited data support this concept in humans.
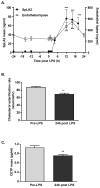
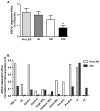
Methods and results: We employed low-dose human endotoxemia to assess the effects of inflammation on HDL and RCT-related parameters in vivo. Endotoxemia induced remodelling of HDL with depletion of pre-β1a HDL particles determined by 2-D gel electrophoresis (-32.2±9.3% at 24 h, p<0.05) as well as small (-23.0±5.1%, p<0.01, at 24 h) and medium (-57.6±8.0% at 16 h, p<0.001) HDL estimated by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). This was associated with induction of class II secretory phospholipase A2 (~36 fold increase) and suppression of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase activity (-20.8±3.4% at 24 h, p<0.01) and cholesterol ester transfer protein mass (-22.2±6.8% at 24 h, p<0.001). The HDL fraction, isolated following endotoxemia, had reduced capacity to efflux cholesterol in vitro from SR-BI and ABCA1, but not ABCG1 transporter cell models.
Conclusions: These data support the concept that "atherogenic-HDL dysfunction" and impaired RCT occur in human inflammatory syndromes, largely independent of changes in plasma HDL-C and ApoA-I levels.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Wang X, Rader DJ. Molecular regulation of macrophage reverse cholesterol transport. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2007;22:368–372. - PubMed
-
- van der Westhuyzen DR, de Beer FC, Webb NR. HDL cholesterol transport during inflammation. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2007;18:147–151. - PubMed
-
- Khovidhunkit W, Kim MS, Memon RA, Shigenaga JK, Moser AH, Feingold KR, Grunfeld C. Effects of infection and inflammation on lipid and lipoprotein metabolism: mechanisms and consequences to the host. J Lipid Res. 2004;45:1169–1196. - PubMed
-
- Hudgins LC, Parker TS, Levine DM, Gordon BR, Saal SD, Jiang XC, Seidman CE, Tremaroli JD, Lai J, Rubin AL. A single intravenous dose of endotoxin rapidly alters serum lipoproteins and lipid transfer proteins in normal volunteers. J Lipid Res. 2003;44:1489–1498. - PubMed
-
- Levels JH, Pajkrt D, Schultz M, Hoek FJ, van Tol A, Meijers JC, van Deventer SJ. Alterations in lipoprotein homeostasis during human experimental endotoxemia and clinical sepsis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1771:1429–1438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

