Hedgehog signaling inhibition by the small molecule smoothened inhibitor GDC-0449 in the bone forming prostate cancer xenograft MDA PCa 118b
- PMID: 22457212
- PMCID: PMC4977841
- DOI: 10.1002/pros.22517
Hedgehog signaling inhibition by the small molecule smoothened inhibitor GDC-0449 in the bone forming prostate cancer xenograft MDA PCa 118b
Abstract
Background: Hedgehog signaling is a stromal-mesenchymal pathway central to the development and homeostasis of both the prostate and the bone. Aberrant Hedgehog signaling activation has been associated with prostate cancer aggressiveness. We hypothesize that Hedgehog pathway is a candidate therapeutic target in advanced prostate cancer. We confirm increased Hedgehog signaling in advanced and bone metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer and examine the pharmacodynamic effect of Smoothened inhibition by the novel reagent GDC-0449 in an experimental prostate cancer model.
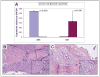
Methods: Hedgehog signaling component expression was assessed in tissue microarrays of high grade locally advanced and bone metastatic disease. Male SCID mice subcutaneously injected with the bone forming xenograft MDA PCa 118b were treated with GDC-0449. Hedgehog signaling in the tumor microenvironment was assessed by proteomic and species specific RNA expression and compared between GDC-0449 treated and untreated animals.
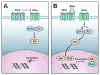
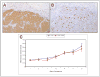
Results: We observe Hedgehog signaling in high grade locally advanced and bone marrow infiltrating disease. Evidence of paracrine activation of Hedgehog signaling in the tumor xenograft, was provided by increased Sonic Hedgehog expression in human tumor epithelial cells, coupled with increased Gli1 and Patched1 expression in the murine stromal compartment, while normal murine stroma did not exhibit Hh signaling expression. GDC-0449 treatment attenuated Hh signaling as evidenced by reduced expression of Gli1 and Ptch1. Reduction in proliferation (Ki67) was observed with no change in tumor volume.
Conclusions: GDC-0449 treatment is pharmacodynamically effective as evidenced by paracrine Hedgehog signaling inhibition and results in tumor cell proliferation reduction. Understanding these observations will inform the clinical development of therapy based on Hedgehog signaling inhibition.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of hedgehog signaling improves the anti-carcinogenic effects of docetaxel in prostate cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Feb 28;6(6):3887-903. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2932. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25682877 Free PMC article.
-
TAK-441, a novel investigational smoothened antagonist, delays castration-resistant progression in prostate cancer by disrupting paracrine hedgehog signaling.Int J Cancer. 2013 Oct 15;133(8):1955-66. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28193. Epub 2013 May 6. Int J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23564295
-
BMP4 promotes prostate tumor growth in bone through osteogenesis.Cancer Res. 2011 Aug 1;71(15):5194-203. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4374. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21670081 Free PMC article.
-
Vismodegib.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018;211:125-139. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-91442-8_9. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30069764 Review.
-
Novel therapies for metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011 Nov 16;103(22):1665-75. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djr362. Epub 2011 Sep 13. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011. PMID: 21917607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hedgehog signaling in prostate cancer and its therapeutic implication.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jul 4;14(7):13979-4007. doi: 10.3390/ijms140713979. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23880852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA m6A Methyltransferase METTL3 Promotes The Growth Of Prostate Cancer By Regulating Hedgehog Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Nov 5;12:9143-9152. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S226796. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31806999 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of hedgehog signaling improves the anti-carcinogenic effects of docetaxel in prostate cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Feb 28;6(6):3887-903. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2932. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25682877 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of Prostate Cancer Patient-Derived Xenografts to Investigate Mechanisms of Novel Treatments and Treatment Resistance.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1786:1-27. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7845-8_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29786784 Free PMC article.
-
Prostate cancer: Smoothened inhibition reduces tumor cell proliferation.Nat Rev Urol. 2012 Apr 17;9(5):237. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2012.71. Nat Rev Urol. 2012. PMID: 22508454 No abstract available.
References
-
- Efstathiou E, Troncoso P, Wen S, Do KA, Pettaway CA, Pisters LL, McDonnell TJ, Logothetis CJ. Initial modulation of the tumor microenvironment accounts for thalidomide activity in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(4):1224–1231. - PubMed
-
- Cano P, Godoy A, Escamilla R, Dhir R, Onate SA. Stromal-epithelial cell interactions and androgen receptor-coregulator recruitment is altered in the tissue microenvironment of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67(2):511–519. - PubMed
-
- Varjosalo M, Taipale J. Hedgehog: functions and mechanisms. Genes Dev. 2008;22(18):2454–2472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

