Identical consensus sequence and conserved genomic polymorphism of hepatitis E virus during controlled interspecies transmission
- PMID: 22457521
- PMCID: PMC3372222
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.06843-11
Identical consensus sequence and conserved genomic polymorphism of hepatitis E virus during controlled interspecies transmission
Abstract
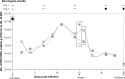
High-throughput sequencing of bile and feces from two pigs experimentally infected with human hepatitis E virus (HEV) of genotype 3f revealed the same full-length consensus sequence as in the human sample. Twenty-nine percent of polymorphic sites found in HEV from the human sample were conserved throughout the infection of the heterologous host. The interspecies transmission of HEV quasispecies is the result of a genomic negative-selection pressure on random mutations which can be deleterious to the viral population. HEV intrahost nucleotide diversity was found to be in the lower range of other human RNA viruses but correlated with values found for zoonotic viruses. HEV transmission between humans and pigs does not seem to be modulated by host-specific mutations, suggesting that adaptation is mainly regulated by ecological drivers.
Figures


References
-
- Arankalle VA, Chobe LP, Chadha MS. 2006. Type-IV Indian swine HEV infects rhesus monkeys. J. Viral Hepat. 13:742–745 - PubMed
-
- Balayan MS, Usmanov RK, Zamyatina NA, Djumalieva DI, Karas FR. 1990. Brief report: experimental hepatitis E infection in domestic pigs. J. Med. Virol. 32:58–59 - PubMed
-
- Belshaw R, Sanjuán R, Pybus OG. 2011. Viral mutation and substitution: units and levels. Curr. Opin. Virol. 1:430–435 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

