A scalable fabrication process of polymer microneedles
- PMID: 22457598
- PMCID: PMC3310406
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S28511
A scalable fabrication process of polymer microneedles
Abstract
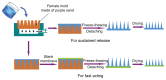
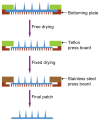
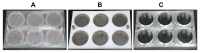
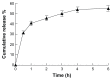
While polymer microneedles may easily be fabricated by casting a solution in a mold, either centrifugation or vacuumizing is needed to pull the viscous polymer solution into the microholes of the mold. We report a novel process to fabricate polymer microneedles with a one-sided vacuum using a ceramic mold that is breathable but water impermeable. A polymer solution containing polyvinyl alcohol and polysaccharide was cast in a ceramic mold and then pulled into the microholes by a vacuum applied to the opposite side of the mold. After cross-linking and solidification through freeze-thawing, the microneedle patch was detached from the mold and transferred with a specially designed instrument for the drying process, during which the patch shrank evenly to form an array of regular and uniform needles without deformation. Moreover, the shrinkage of the patches helped to reduce the needles' size to ease microfabrication of the male mold. The dried microneedle patches were finally punched to the desired sizes to achieve various properties, including sufficient strength to penetrate skin, microneedles-absorbed water-swelling ratios, and drug-release kinetics. The results showed that the microneedles were strong enough to penetrate pigskin and that their performance was satisfactory in terms of swelling and drug release.
Keywords: ceramic mold; polymer microneedles; polyvinyl alcohol; swelling.
Figures





References
-
- Henry S, McAllister DV, Allen MG, Prausnitz MR. Microfabricated microneedles: a novel approach to transdermal drug delivery. J Pharm Sci. 1998;87(8):922–925. - PubMed
-
- Prausnitz MR. Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004;56(5):581–587. - PubMed
-
- Bartus RT, Tracy MA, Emerich DF, Zale SE. Sustained delivery of proteins for novel therapeutic products. Science. 1998;281(5380):1161–1162. - PubMed
-
- Wilke N, Mulcahy A, Ye SR, Morrissey A. Process optimization and characterization of silicon microneedles fabricated by wet etch technology. Microelectron J. 2005;36(7):650–656.
-
- Chabri F, Bouris K, Jones T, et al. Microfabricated silicon microneedles for nonviral cutaneous gene delivery. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150(5):869–877. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

