TWIST represses estrogen receptor-alpha expression by recruiting the NuRD protein complex in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 22457607
- PMCID: PMC3314193
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.4164
TWIST represses estrogen receptor-alpha expression by recruiting the NuRD protein complex in breast cancer cells
Abstract
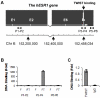
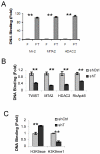
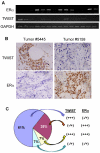
Loss of estrogen receptor α (ERα) expression and gain of TWIST (TWIST1) expression in breast tumors correlate with increased disease recurrence and metastasis and poor disease-free survival. However, the molecular and functional regulatory relationship between TWIST and ERα are unclear. In this study, we found TWIST was associated with a chromatin region in intron 7 of the human ESR1 gene coding for ERα. This association of TWIST efficiently recruited the nucleosome remodeling and deacetylase (NuRD) repressor complex to this region, which subsequently decreased histone H3K9 acetylation, increased histone H3K9 methylation and repressed ESR1 expression in breast cancer cells. In agreement with these molecular events, TWIST expression was inversely correlated with ERα expression in both breast cancer cell lines and human breast ductal carcinomas. Forced expression of TWIST in TWIST-negative and ERα-positive breast cancer cells such as T47D and MCF-7 cells reduced ERα expression, while knockdown of TWIST in TWIST-positive and ERα-negative breast cancer cells such as MDA-MB-435 and 4T1 cells increased ERα expression. Furthermore, inhibition of histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity including the one in NuRD complex significantly increased ERα expression in MDA-MB-435 and 4T1 cells. HDAC inhibition together with TWIST knockdown did not further increase ERα expression in 4T1 and MDA-MB-435 cells. These results demonstrate that TWIST/NuRD represses ERα expression in breast cancer cells. Therefore, TWIST may serve as a potential molecular target for converting ERα-negative breast cancers to ERα-positive breast cancers, allowing these cancers to restore their sensitivity to endocrine therapy with selective ERα antagonists such as tamoxifen and raloxifene.
Keywords: ERα; NuRD complex; TWIST; breast cancer; gene repression.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

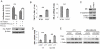
References
-
- Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL. et al. Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell. 2004;117:927–39. - PubMed
-
- Cheng GZ, Zhang W, Wang LH. Regulation of cancer cell survival, migration, and invasion by Twist: AKT2 comes to interplay. Cancer Res. 2008;68:957–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

