Genital HSV-2 infection induces short-term NK cell memory
- PMID: 22457721
- PMCID: PMC3310819
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032821
Genital HSV-2 infection induces short-term NK cell memory
Abstract
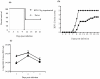
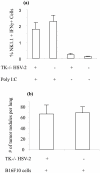
NK cells are known as innate immune cells that lack immunological memory. Recently, it has been shown that NK cells remember encounters with chemical haptens that induce contact hypersensitivity and cytomegalovirus infection. Here, we show the existence of NK cell memory following HSV-2 infection. Stimulation with HSV-2 Ags led to higher IFNγ production in NK cells that were exposed 30 days previously to HSV-2, compared to NK cells from naïve mice. More importantly, this increased production of IFNγ in NK cells was independent of B- and T- lymphocytes and specific for the HSV-2 Ags. We also showed that previously exposed NK cells in a B- and T-lymphocyte free environment mediate protection against HSV-2 infection and they are necessary for the protection of mice against HSV-2 infection. Collectively, NK cells remember prior HSV-2 encounters independent of B- and T- lymphocytes leading to protection against HSV-2 mediated morbidity and mortality upon re-exposure.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Vivier E, Nunes JA, Vely F. Natural killer cell signaling pathways. Science. 2004;306:1517–1519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

