Diabetes-associated common genetic variation and its association with GLP-1 concentrations and response to exogenous GLP-1
- PMID: 22461567
- PMCID: PMC3331759
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-1732
Diabetes-associated common genetic variation and its association with GLP-1 concentrations and response to exogenous GLP-1
Abstract
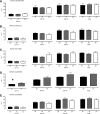
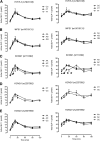
The mechanisms by which common genetic variation predisposes to type 2 diabetes remain unclear. The disease-associated variants in TCF7L2 (rs7903146) and WFS1 (rs10010131) have been shown to affect response to exogenous glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1), while variants in KCNQ1 (rs151290, rs2237892, and rs2237895) alter endogenous GLP-1 secretion. We set out to validate these observations using a model of GLP-1-induced insulin secretion. We studied healthy individuals using a hyperglycemic clamp and GLP-1 infusion. In addition, we measured active and total GLP-1 in response to an oral challenge in nondiabetic subjects. After genotyping the relevant single nucleotide polymorphisms, generalized linear regression models and repeated-measures ANCOVA models incorporating potential confounders, such as age and BMI, were used to assess the associations, if any, of response with genotype. These variants did not alter GLP-1 concentrations in response to oral intake. No effects on β-cell responsiveness to hyperglycemia and GLP-1 infusion were apparent. Diabetes-associated variation (T allele at rs7903146) in TCF7L2 may impair the ability of hyperglycemia to suppress glucagon (45 ± 2 vs. 47 ± 2 vs. 60 ± 5 ng/L for CC, CT, and TT, respectively, P = 0.02). In nondiabetic subjects, diabetes-associated genetic variation does not alter GLP-1 concentrations after an oral challenge or its effect on insulin secretion.
Figures


References
-
- Drucker DJ. Glucagon-like peptides: regulators of cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Mol Endocrinol 2003;17:161–171 - PubMed
-
- Nauck MA, Vardarli I, Deacon CF, Holst JJ, Meier JJ. Secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in type 2 diabetes: what is up, what is down? Diabetologia 2011;54:10–18 - PubMed
-
- Fritsche A, Stefan N, Hardt E, Häring H, Stumvoll M. Characterisation of beta-cell dysfunction of impaired glucose tolerance: evidence for impairment of incretin-induced insulin secretion. Diabetologia 2000;43:852–858 - PubMed
-
- Chen M, Bergman RN, Pacini G, Porte D., Jr Pathogenesis of age-related glucose intolerance in man: insulin resistance and decreased beta-cell function. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1985;60:13–20 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

