Role of biofeedback in optimizing psychomotor performance in sports
- PMID: 22461963
- PMCID: PMC3307964
- DOI: 10.5812/asjsm.34722
Role of biofeedback in optimizing psychomotor performance in sports
Abstract
Purpose: Biofeedback is an emerging tool to acquire and facilitate physiological and psychological domains of the human body like response time and concentration. Thus, the present study aims at determining the reconstitution of psychomotor and performance skills in basketball players through biofeedback training.
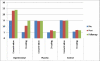
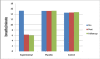
Methods: Basketball players (N=30) with different levels of expertise (university, state and national) aged 18-28 years (both male and female) were randomly divided into 3 equal groups - Experimental group, Placebo group and Control group. The experimental group received Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback training for 10 consecutive days for 20 minutes that included breathing at individual's resonant frequency through a pacing stimulus; Placebo group was shown motivational video clips for 10 consecutive days for 10 minutes, whereas Control group was not given any intervention. At session 1, 10 and 1month follow up, heart rate variability, respiration rate, response time (reaction and movement time), concentration and shooting performance were assessed.
Results: Two way repeated measure ANOVA was used to simultaneously compare within and between group differences. Response time, concentration, heart rate variability, respiration rate and shooting differences were statistically significant in each group along with interaction of group and time (P<0.001). Also, all the measures showed statistically significant inter group difference (P<0.05).
Conclusion: The results of the study suggest that biofeedback training may help to train stressed athletes to acquire a control over their psychophysiological processes, thus helping an athlete to perform maximally.
Keywords: Concentration; Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback; Psychomotor Performance; Response Time; Shooting.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effect of heart rate variability biofeedback on performance psychology of basketball players.Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2012 Jun;37(2):131-44. doi: 10.1007/s10484-012-9185-2. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2012. PMID: 22402913 Clinical Trial.
-
The Effect of Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback on Basketball Performance Tests.Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2023 Dec;48(4):461-470. doi: 10.1007/s10484-023-09600-7. Epub 2023 Jul 25. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2023. PMID: 37490184
-
Can biofeedback training of psychophysiological responses enhance athletes' sport performance? A practitioner's perspective.Phys Sportsmed. 2015 Jul;43(3):287-99. doi: 10.1080/00913847.2015.1069169. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Phys Sportsmed. 2015. PMID: 26200172
-
Effects of Mindfulness Practice on Performance-Relevant Parameters and Performance Outcomes in Sports: A Meta-Analytical Review.Sports Med. 2017 Nov;47(11):2309-2321. doi: 10.1007/s40279-017-0752-9. Sports Med. 2017. PMID: 28664327 Review.
-
Factors that influence performance in Olympic air-rifle and small-bore shooting: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 31;16(3):e0247353. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247353. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33788853 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pre-competition mental energy and performance relationships among physically disabled table tennis players.PeerJ. 2022 Apr 14;10:e13294. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13294. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35441058 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the six factors model of athletic mental energy in mediating athletes' well-being in competitive sports.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 5;14(1):2974. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53065-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38316915 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Psychological and Psychosocial Interventions on Sport Performance: A Meta-Analysis.Sports Med. 2017 Jan;47(1):77-99. doi: 10.1007/s40279-016-0552-7. Sports Med. 2017. PMID: 27241124 Review.
-
Psychomotor Abilities of Professional Handball Players.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 May 30;16(11):1909. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16111909. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31151149 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of selected anthropometric parameters on psychomotor abilities among professional Rugby Union players.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2023 Sep 29;15(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s13102-023-00735-y. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 37775800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schmidt RA, Lee TD. Motor control and learning: A behavioral emphasis. 3rd ed. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics; 1999.
-
- Schultz RB, Etnyre B, Mc Arthur JM, et al. Effects of electromyographic biofeedback on reaction time and movement time. Percept Mot Skills. 1987;65:855–9. - PubMed
-
- Namita , Ranjan DP, Shenvi DN. Effect of shift working in reaction time in hospital employees. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010;54:289–293. - PubMed
-
- Senel O, Eroglu H. Correlation between reaction time and speed in elite soccer players. J Exerc Sci Fitness. 2006;4:126–130.
-
- Mannie K. Scholastic Inc, FindArticles.com: Coach and Athletic director; 2011. Feb 23, Improving Quickness Response time 2001. http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m0FIH/is_9_70/ai_n18611822/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
