Detecting early-warning signals for sudden deterioration of complex diseases by dynamical network biomarkers
- PMID: 22461973
- PMCID: PMC3314989
- DOI: 10.1038/srep00342
Detecting early-warning signals for sudden deterioration of complex diseases by dynamical network biomarkers
Abstract
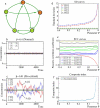
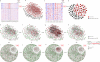
Considerable evidence suggests that during the progression of complex diseases, the deteriorations are not necessarily smooth but are abrupt, and may cause a critical transition from one state to another at a tipping point. Here, we develop a model-free method to detect early-warning signals of such critical transitions, even with only a small number of samples. Specifically, we theoretically derive an index based on a dynamical network biomarker (DNB) that serves as a general early-warning signal indicating an imminent bifurcation or sudden deterioration before the critical transition occurs. Based on theoretical analyses, we show that predicting a sudden transition from small samples is achievable provided that there are a large number of measurements for each sample, e.g., high-throughput data. We employ microarray data of three diseases to demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. The relevance of DNBs with the diseases was also validated by related experimental data and functional analysis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Detecting tissue-specific early warning signals for complex diseases based on dynamical network biomarkers: study of type 2 diabetes by cross-tissue analysis.Brief Bioinform. 2014 Mar;15(2):229-43. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbt027. Epub 2013 Apr 25. Brief Bioinform. 2014. PMID: 23620135
-
Detecting early-warning signals of type 1 diabetes and its leading biomolecular networks by dynamical network biomarkers.BMC Med Genomics. 2013;6 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S8. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-6-S2-S8. Epub 2013 May 7. BMC Med Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23819540 Free PMC article.
-
Detection for disease tipping points by landscape dynamic network biomarkers.Natl Sci Rev. 2019 Jul;6(4):775-785. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwy162. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Natl Sci Rev. 2019. PMID: 34691933 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamical network biomarkers: Theory and applications.Gene. 2022 Jan 15;808:145997. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2021.145997. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Gene. 2022. PMID: 34626720 Review.
-
Early diagnosis of complex diseases by molecular biomarkers, network biomarkers, and dynamical network biomarkers.Med Res Rev. 2014 May;34(3):455-78. doi: 10.1002/med.21293. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Med Res Rev. 2014. PMID: 23775602 Review.
Cited by
-
Elucidating tumor heterogeneity from spatially resolved transcriptomics data by multi-view graph collaborative learning.Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 10;13(1):5962. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33619-9. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36216831 Free PMC article.
-
Establishing Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance as an Independent Pre-Disease State of Multiple Myeloma Using Raman Spectroscopy, Dynamical Network Biomarker Theory, and Energy Landscape Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 26;25(3):1570. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031570. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338848 Free PMC article.
-
Functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for the detection and quantitative analysis of cell surface antigen.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:349408. doi: 10.1155/2013/349408. Epub 2012 Dec 31. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23484112 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling biological systems from molecules to dynamical networks.BMC Syst Biol. 2012;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S1. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-6-S1-S1. Epub 2012 Jul 16. BMC Syst Biol. 2012. PMID: 23046669 Free PMC article.
-
Tracing dynamic biological processes during phase transition.BMC Syst Biol. 2012;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S12. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-6-S1-S12. Epub 2012 Jul 16. BMC Syst Biol. 2012. PMID: 23046764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scheffer M., Carpenter S., Foley J. A., Folke C. &Walker B. Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature 413, 591–596 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Drake M. J. & Griffen D. B. Early warning signals of extinction in deteriorating environments. Nature 467, 456–459 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Kambhu J., Weidman S. & Krishnan N. New Directions for Understanding Systemic Risk: A Report on a Conference Cosponsored by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York and the National Academy of Sciences (The National Academies Press, Washington D.C., 2007).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

