Effect of chronic L-dopa or melatonin treatments after dopamine deafferentation in rats: dyskinesia, motor performance, and cytological analysis
- PMID: 22462019
- PMCID: PMC3302121
- DOI: 10.5402/2012/360379
Effect of chronic L-dopa or melatonin treatments after dopamine deafferentation in rats: dyskinesia, motor performance, and cytological analysis
Abstract
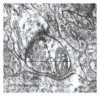
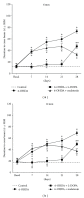
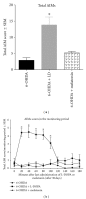
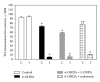
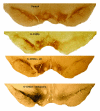
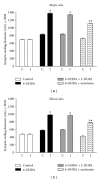
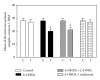
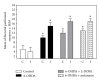
The present study examines the ability of melatonin to protect striatal dopaminergic loss induced by 6-OHDA in a rat model of Parkinson's disease, comparing the results with L-DOPA-treated rats. The drugs were administered orally daily for a month, their therapeutic or dyskinetic effects were assessed by means of abnormal involuntary movements (AIMs) and stepping ability. At the cellular level, the response was evaluated using tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity and striatal ultrastructural changes to compare between L-DOPA-induced AIMs and Melatonin-treated rats. Our findings demonstrated that chronic oral administration of Melatonin improved the alterations caused by the neurotoxin 6-OHDA. Melatonin-treated animals perform better in the motor tasks and had no dyskinetic alterations compared to L-DOPA-treated group. At the cellular level, we found that Melatonin-treated rats showed more TH-positive neurons and their striatal ultrastructure was well preserved. Thus, Melatonin is a useful treatment to delay the cellular and behavioral alterations observed in Parkinson's disease.
Figures

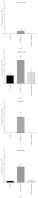

References
-
- Perry TL, Yong VW. Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy and glutathione metabolism in the substantia nigra of patients. Neuroscience Letters . 1986;67(3):269–274. . - PubMed
-
- Saggu H, Cooksey J, Dexter D, et al. A selective increase in particulate superoxide dismutase activity in parkinsonian substantia nigra. Journal of Neurochemistry . 1989;53(3):692–697. . - PubMed
-
- Dexter DT, Wells FR, Lees AJ, et al. Increased nigral iron content and alterations in other metal ions occurring in brain in Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neurochemistry . 1989;52(6):1830–1836. . - PubMed
-
- Alam ZI, Daniel SE, Lees AJ, Marsden DC, Jenner P, Halliwell B. A generalised increase in protein carbonyls in the brain in Parkinson’s but not incidental Lewy body disease. Journal of Neurochemistry . 1997;69(3):1326–1329. . - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

