GTPase networks in membrane traffic
- PMID: 22463690
- PMCID: PMC3708692
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-052810-093700
GTPase networks in membrane traffic
Abstract
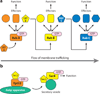
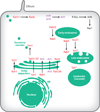
Members of the Rab or ARF/Sar branches of the Ras GTPase superfamily regulate almost every step of intracellular membrane traffic. A rapidly growing body of evidence indicates that these GTPases do not act as lone agents but are networked to one another through a variety of mechanisms to coordinate the individual events of one stage of transport and to link together the different stages of an entire transport pathway. These mechanisms include guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) cascades, GTPase-activating protein (GAP) cascades, effectors that bind to multiple GTPases, and positive-feedback loops generated by exchange factor-effector interactions. Together these mechanisms can lead to an ordered series of transitions from one GTPase to the next. As each GTPase recruits a unique set of effectors, these transitions help to define changes in the functionality of the membrane compartments with which they are associated.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Crosstalk of Arf and Rab GTPases en route to cilia.Small GTPases. 2013 Apr-Jun;4(2):70-7. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.24396. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Small GTPases. 2013. PMID: 23567335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arf GTPase regulation through cascade mechanisms and positive feedback loops.FEBS Lett. 2013 Jun 27;587(13):2028-35. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.05.015. Epub 2013 May 16. FEBS Lett. 2013. PMID: 23684643 Review.
-
The role of ADP-ribosylation factor and SAR1 in vesicular trafficking in plants.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Jul 1;1664(1):9-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.04.005. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15238254 Review.
-
ArfGAP1 acts as a GTPase-activating protein for human ADP-ribosylation factor-like 1 protein.FASEB J. 2021 Apr;35(4):e21337. doi: 10.1096/fj.202000818RR. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 33715220
-
Rab GTPase localization and Rab cascades in Golgi transport.Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Dec 1;40(6):1373-7. doi: 10.1042/BST20120168. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 23176483 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of Rab8 guanine nucleotide exchange factor Rabin8 by ERK1/2 in response to EGF signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jan 6;112(1):148-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1412089112. Epub 2014 Dec 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25535387 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk of Arf and Rab GTPases en route to cilia.Small GTPases. 2013 Apr-Jun;4(2):70-7. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.24396. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Small GTPases. 2013. PMID: 23567335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is the model of signal amplification by GPCRs/GEFs activating multiple GTPases relevant to a broad spectrum of heterotrimeric and RAS superfamily GTPases?Cell Logist. 2014 May 1;4(2):e943602. doi: 10.4161/21592780.2014.943602. eCollection 2014 Jun. Cell Logist. 2014. PMID: 25610716 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insight into an Arl1-ArfGEF complex involved in Golgi recruitment of a GRIP-domain golgin.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 2;15(1):1942. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46304-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38431634 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the Rab exchange factor Sec2p directs a switch in regulatory binding partners.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Dec 10;110(50):19995-20002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1320029110. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24248333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schalk I, Zeng K, Wu SK, Stura EA, Matteson J, et al. Structure and mutational analysis of Rab GDP-dissociation inhibitor. Nature. 1996;381(6577):42–48. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg J. Structural basis for activation of ARF GTPase: mechanisms of guanine nucleotide exchange and GTP-myristoyl switching. Cell. 1998;95(2):237–248. - PubMed
-
- Gillingham AK, Munro S. The small G proteins of the Arf family and their regulators. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007;23:579–611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

