The potential economic value of a Staphylococcus aureus vaccine among hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 22464963
- PMCID: PMC3371356
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.03.031
The potential economic value of a Staphylococcus aureus vaccine among hemodialysis patients
Abstract
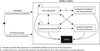
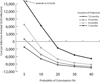
Staphylococcus aureus infections are a substantial problem for hemodialysis patients. Several vaccine candidates are currently under development, with hemodialysis patients being one possible target population. To determine the potential economic value of an S. aureus vaccine among hemodialysis patients, we developed a Markov decision analytic computer simulation model. When S. aureus colonization prevalence was 1%, the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of vaccination was ≤$25,217/quality-adjusted life year (QALY). Vaccination became more cost-effective as colonization prevalence, vaccine efficacy, or vaccine protection duration increased or vaccine cost decreased. Even at 10% colonization prevalence, a 25% efficacious vaccine costing $100 prevented 29 infections, 21 infection-related hospitalizations, and 9 inpatient deaths per 1000 vaccinated HD patients. Our results suggest that an S. aureus vaccine would be cost-effective (i.e., ICERs ≤ $50,000/QALY) among hemodialysis patients over a wide range of S. aureus prevalence, vaccine costs and efficacies, and vaccine protection durations and delineate potential target parameters for such a vaccine.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Fitzgibbons LN, Puls DL, Mackay K, Forrest GN. Management of gram-positive coccal bacteremia and hemodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011 Apr;57(4):624–640. - PubMed
-
- Sexton DJ. Vascular access infections in patients undergoing dialysis with special emphasis on the role and treatment of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2001 Sep;15(3):731–742. vii. - PubMed
-
- Lowy FD. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med. 1998 Aug 20;339(8):520–532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical