Novel peptide for attenuation of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension via modulation of nitric oxide release and phosphodiesterase -5 activity
- PMID: 22465621
- PMCID: PMC3335268
- DOI: 10.1016/j.peptides.2012.03.009
Novel peptide for attenuation of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension via modulation of nitric oxide release and phosphodiesterase -5 activity
Abstract
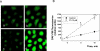
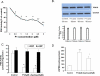
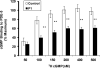
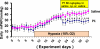
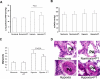
Pulmonary vascular endothelial nitric oxide (NO) synthase (eNOS)-derived NO is the major stimulant of cyclic guanosine 5'-monophosphate (cGMP) production and NO/cGMP-dependent vasorelaxation in the pulmonary circulation. We recently synthesized multiple peptides and reported that an eleven amino acid (SSWRRKRKESS) peptide (P1) but not scrambled P1 stimulated the catalytic activity but not expression of eNOS and causes NO/cGMP-dependent sustained vasorelaxation in isolated pulmonary artery (PA) segments and in lung perfusion models. Since cGMP levels can also be elevated by inhibition of phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE-5), this study was designed to test the hypothesis that P1-mediated vesorelaxation is due to its unique dual action as NO-releasing PDE-5 inhibitor in the pulmonary circulation. Treatment of porcine PA endothelial cells (PAEC) with P1 caused time-dependent increase in intracellular NO release and inhibition of the catalytic activity of cGMP-specific PDE-5 but not PDE-5 protein expression leading to increased levels of cGMP. Acute hypoxia-induced PA vasoconstriction ex vivo and continuous telemetry monitoring of hypoxia (10% oxygen)-induced elevated PA pressure in freely moving rats were significantly restored by administration of P1. Chronic hypoxia (10% oxygen for 4 weeks)-induced alterations in PA perfusion pressure, right ventricular hypertrophy, and vascular remodeling were attenuated by P1 treatment. These results demonstrate the potential therapeutic effects of P1 to prevent and/or arrest the progression of hypoxia-induced PAH via NO/cGMP-dependent modulation of hemodynamic and vascular remodeling in the pulmonary circulation.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Colbran JL, Francis SH, Leach AB, Thomas MK, Jiang H, McAllister LM, Corbin JD. A phenylalanine in peptide substrates provides for selectivity between cGMP- and cAMP-dependent protein kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1992;267:9589–9594. - PubMed
-
- D'Alonzo GE, Barst RJ, Ayres SM, Bergofsky EH, Brundage BH, Detre KM, Fishman AP, Goldring RM, Groves BM, Kernis JT, Levy PS, Pietra GG, Reid LM, Reeves JT, Rich S, Vreim CE, Williams GW, Wu M. Survival in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension:results from a national prospective registry. Ann. Intern. Med. 1991;115:343–349. - PubMed
-
- Davis MG, Fulton GJ, Hagen PO. Clinical biology of nitric oxide. Br. J. Surg. 1995;82:1598–1610. - PubMed
-
- Farber HW, Loscalzo J. Pulmonary arterial hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;351:1655, 1665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

