A combinatorial TIR1/AFB-Aux/IAA co-receptor system for differential sensing of auxin
- PMID: 22466420
- PMCID: PMC3331960
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.926
A combinatorial TIR1/AFB-Aux/IAA co-receptor system for differential sensing of auxin
Abstract
The plant hormone auxin regulates virtually every aspect of plant growth and development. Auxin acts by binding the F-box protein transport inhibitor response 1 (TIR1) and promotes the degradation of the AUXIN/INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID (Aux/IAA) transcriptional repressors. Here we show that efficient auxin binding requires assembly of an auxin co-receptor complex consisting of TIR1 and an Aux/IAA protein. Heterologous experiments in yeast and quantitative IAA binding assays using purified proteins showed that different combinations of TIR1 and Aux/IAA proteins form co-receptor complexes with a wide range of auxin-binding affinities. Auxin affinity seems to be largely determined by the Aux/IAA. As there are 6 TIR1/AUXIN SIGNALING F-BOX proteins (AFBs) and 29 Aux/IAA proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana, combinatorial interactions may result in many co-receptors with distinct auxin-sensing properties. We also demonstrate that the AFB5-Aux/IAA co-receptor selectively binds the auxinic herbicide picloram. This co-receptor system broadens the effective concentration range of the hormone and may contribute to the complexity of auxin response.
Figures
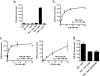
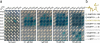

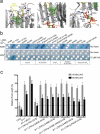
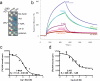
Comment in
-
Plant signaling: Deconstructing auxin sensing.Nat Chem Biol. 2012 Apr 17;8(5):415-6. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.943. Nat Chem Biol. 2012. PMID: 22510662 No abstract available.
References
-
- Auxin Signaling-From Synthesis to Systems Biology. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press; New York: 2011.
-
- Weijers D, et al. Auxin triggers transient local signaling for cell specification in Arabidopsis embryogenesis. Dev Cell. 2006;10:265–70. - PubMed
-
- Holland JJ, Roberts D, Liscum E. Understanding phototropism: from Darwin to today. J Exp Bot. 2009;60:1969–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- BB/F014651/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 CA107134/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM07270/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- BB/F007418/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

