Effects of postnatal dexamethasone or hydrocortisone in a rat model of antenatal lipopolysaccharide and neonatal hyperoxia exposure
- PMID: 22468103
- PMCID: PMC3314852
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.4.395
Effects of postnatal dexamethasone or hydrocortisone in a rat model of antenatal lipopolysaccharide and neonatal hyperoxia exposure
Abstract
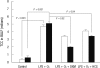
The aim of our study was to investigate the differential effects of dexamethasone (DXM) and hydrocortisone (HCS) on somatic growth and postnatal lung development in a rat model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). A rat model of BPD was induced by administering intra-amniotic lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and postnatal hyperoxia. The rats were treated with a 6-day (D1-D6) tapering course of DXM (starting dose 0.5 mg/kg/day), HCS (starting dose 2 mg/kg/day), or an equivalent volume of normal saline. DXM treatment in a rat model of BPD induced by LPS and hyperoxia was also associated with a more profound weight loss compared to control and LPS + O(2) groups not exposed to corticosteroid, whereas HCS treatment affected body weight only slightly. Examination of lung morphology showed worse mean cord length in both LPS + O(2) + DXM and LPS + O(2) + HCS groups as compared to the LPS + O(2) alone group, and the LPS + O(2) + DXM group had thicker alveolar walls than the LPS + O(2) group at day 14. The HCS treatment was not significantly associated with aberrant alveolar wall thickening and retarded somatic growth. The use of postnatal DXM or HCS in a rat model of BPD induced by intra-amniotic LPS and postnatal hyperoxia appeared detrimental to lung growth, but there was less effect in the case of HCS. These findings suggest that effect of HCS on somatic growth and pulmonary outcome may be better tolerated in neonates for preventing and/or treating BPD.
Keywords: Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia; Dexamethasone; Hydrocortisone; Lung Development.
Figures


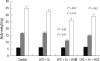

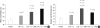
Similar articles
-
Effects of postnatal corticosteroids on lung development in newborn animals. A systematic review.Pediatr Res. 2024 Oct;96(5):1141-1152. doi: 10.1038/s41390-024-03114-6. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Pediatr Res. 2024. PMID: 38493255 Free PMC article.
-
Association of increased pulmonary interleukin-6 with the priming effect of intra-amniotic lipopolysaccharide on hyperoxic lung injury in a rat model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Neonatology. 2010 Jun;98(1):23-32. doi: 10.1159/000263056. Epub 2009 Dec 2. Neonatology. 2010. PMID: 19955834
-
Serial changes of lung morphology and biochemical profiles in a rat model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia induced by intra-amniotic lipopolysaccharide and postnatal hyperoxia.J Perinat Med. 2010 Nov;38(6):675-81. doi: 10.1515/jpm.2010.091. Epub 2010 Aug 13. J Perinat Med. 2010. PMID: 20707615
-
[Increased apoptosis after intra-amniotic endotoxin priming plus hyperoxic exposure in lungs of preterm newborn rats].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2009 Oct;47(10):767-73. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 20021812 Chinese.
-
When prenatal infection meets postnatal hyperoxia: Better models for bronchopulmonary dysplasia and its therapeutic approaches.Chin Med J Pulm Crit Care Med. 2024 Dec 13;2(4):289-292. doi: 10.1016/j.pccm.2024.11.002. eCollection 2024 Dec. Chin Med J Pulm Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 39834586 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: Crosstalk Between PPARγ, WNT/β-Catenin and TGF-β Pathways; The Potential Therapeutic Role of PPARγ Agonists.Front Pediatr. 2019 May 3;7:176. doi: 10.3389/fped.2019.00176. eCollection 2019. Front Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31131268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dose-dependent effects of glucocorticoids on pulmonary vascular development in a murine model of hyperoxic lung injury.Pediatr Res. 2016 May;79(5):759-65. doi: 10.1038/pr.2016.1. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Pediatr Res. 2016. PMID: 26756781 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological and molecular aspects of lung development.Histol Histopathol. 2025 Apr;40(4):411-430. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-807. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Histol Histopathol. 2025. PMID: 39344418 Review.
-
Rosiglitazone, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ agonist, restores alveolar and pulmonary vascular development in a rat model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Yonsei Med J. 2014 Jan;55(1):99-106. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.1.99. Yonsei Med J. 2014. PMID: 24339293 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of postnatal corticosteroids on lung development in newborn animals. A systematic review.Pediatr Res. 2024 Oct;96(5):1141-1152. doi: 10.1038/s41390-024-03114-6. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Pediatr Res. 2024. PMID: 38493255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yoder MC, Jr, Chua R, Tepper R. Effect of dexamethasone on pulmonary inflammation and pulmonary function of ventilator-dependent infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991;143:1044–1048. - PubMed
-
- Halliday HL. Clinical trials of postnatal corticosteroids: inhaled and systemic. Biol Neonate. 1999;76:29–40. - PubMed
-
- Halliday HL, Ehrenkranz RA, Doyle LW. Early postnatal (< 96 hours) corticosteroids for preventing chronic lung disease in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003:CD001146. - PubMed
-
- Halliday HL, Ehrenkranz RA. Moderately early (7-14 days) postnatal corticosteroids for preventing chronic lung disease in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001:CD001144. - PubMed
-
- Doyle LW, Ehrenkranz RA, Halliday HL. Postnatal hydrocortisone for preventing or treating bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants: a systematic review. Neonatology. 2010;98:111–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

