Characteristics of hospitalized children with 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1): a multicenter study in Korea
- PMID: 22468105
- PMCID: PMC3314854
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.4.408
Characteristics of hospitalized children with 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1): a multicenter study in Korea
Abstract
The majority of Korean patients with pandemic influenza A (H1N1) during the 2009 epidemic were under 20 yr of age. The limited data on the clinical characteristics of these children led us to conduct a case note-based investigation of children admitted to 6 university hospitals with 2009 H1N1 influenza. A total of 804 children was enrolled. The median age was 5 yr; 63.8% were males; and 22.4% had at least one chronic underlying disease. Ninety-five of the patients (11.8%) were critically ill and they suffered more from shortness of breath, dyspnea and lymphopenia than the other patients. Among all the patients, 98.8% were treated with antivirals and 73% received treatment within 48 hr of illness onset. All the enrolled patients are alive and appear to have had good outcomes, probably due to the early intervention and antiviral treatment. This study deals with hospitalized children whose diagnoses of influenza A (H1N1) were confirmed, and therefore provides important new information about the clinical patterns of children with influenza A (H1N1) in Korea.
Keywords: Children; Clinical Characteristics; Epidemiology; Korea; Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1).
Figures
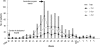
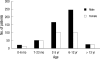
Similar articles
-
Critically ill children with pandemic influenza (H1N1) in pediatric intensive care units in Turkey.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2012 Jan;13(1):e11-7. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e31820aba37. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 21263368
-
Rapid increase in use of antiviral therapy for hospitalized children with influenza during the 2009 H1N1 epidemic.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011 Oct;30(10):895-7. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3182214e28. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011. PMID: 21587093
-
Features associated with severe disease in hospitalized children with 2009 influenza A (H1N1) infection at a university hospital in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.Ann Saudi Med. 2012 Jan-Feb;32(1):53-8. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2012.53. Ann Saudi Med. 2012. PMID: 22156640 Free PMC article.
-
Neurologic complications and outcomes of pandemic (H1N1) 2009 in Korean children.J Korean Med Sci. 2012 Apr;27(4):402-7. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.4.402. Epub 2012 Mar 21. J Korean Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 22468104 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging oseltamivir resistance in seasonal and pandemic influenza A/H1N1.J Clin Virol. 2011 Oct;52(2):70-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2011.05.019. Epub 2011 Jun 17. J Clin Virol. 2011. PMID: 21684202 Review.
Cited by
-
Influenza and the use of oseltamivir in children.Turk Pediatri Ars. 2016 Jun 1;51(2):63-71. doi: 10.5152/TurkPediatriArs.2016.2359. eCollection 2016 Jun. Turk Pediatri Ars. 2016. PMID: 27489462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recurrent plastic bronchitis in a child with 2009 influenza A (H1N1) and influenza B virus infection.J Korean Med Sci. 2012 Sep;27(9):1114-9. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.9.1114. Epub 2012 Aug 22. J Korean Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 22969262 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza in hospitalized children in Ireland in the pandemic period and the 2010/2011 season: risk factors for paediatric intensive-care-unit admission.Epidemiol Infect. 2014 Sep;142(9):1826-35. doi: 10.1017/S0950268813002732. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Epidemiol Infect. 2014. PMID: 24229618 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the reporting quality of influenza outbreaks in the community.Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2017 Nov;11(6):556-563. doi: 10.1111/irv.12516. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2017. PMID: 29054122 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory viruses in neonates hospitalized with acute lower respiratory tract infections.Pediatr Int. 2013 Feb;55(1):49-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200X.2012.03727.x. Epub 2012 Dec 11. Pediatr Int. 2013. PMID: 22978535 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hospitalized patients with novel influenza A (H1N1) virus infection: California, April-May, 2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58:536–541. - PubMed
-
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Analysis of reported pandemic influenza (A/H1N1 2009) virus infections in Korea: From April, 2009 through August, 2010. Public Health Wkly Rep. 2010;3:638–642.
-
- Bettinger JA, Sauvé LJ, Scheifele DW, Moore D, Vaudry W, Tran D, Halperin SA, Pelletier L. Pandemic influenza in Canadian children: a summary of hospitalized pediatric cases. Vaccine. 2010;28:3180–3184. - PubMed
-
- Calitri C, Gabiano C, Garazzino S, Pinon M, Zoppo M, Cuozzo M, Scolfaro C, Tovo PA. Clinical features of hospitalised children with 2009 H1N1 influenza virus infection. Eur J Pediatr. 2010;169:1511–1515. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

