Correlation between lower urinary tract symptoms and premature ejaculation in Korean men older than 40 years old [corrected]
- PMID: 22468215
- PMCID: PMC3312068
- DOI: 10.4111/kju.2012.53.3.189
Correlation between lower urinary tract symptoms and premature ejaculation in Korean men older than 40 years old [corrected]
Erratum in
- Korean J Urol. 2014 Jun;55(6):434
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the correlation between lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and premature ejaculation (PE) in Korean men older than 40 years.
Materials and methods: In total, 258 men older than 40 years completed the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS; total score, storage symptoms [ST], and voiding symptoms [VD]), a 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5), and the Premature Ejaculation Diagnostic Tool (PEDT). The study examined the relationship between LUTS and PE. In the PEDT, PE is defined as a score ≥11.
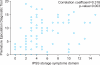
Results: The prevalence of PE was 29.1% with the PEDT versus a self-reported value of 49.5%. The prevalence of PE was 30.9% in 40 to 59-year-old men (21.3%) and 28.1% in 60 to 79 year-old men (78.7%). In men 40 to 59 and 60 to 79 years old, the mean PEDT, IPSS, and IIEF-5 scores were 8.65 and 7.88, 13.5 and 12.38, and 15.83 and 13.69, respectively. No significant correlations were observed between the total and subscale scores of the IPSS (p=0.204) and the PEDT (p=0.309) with increasing age, whereas a significant negative correlation was detected between the IIEF-5 and age (p=0.002). The PEDT score was significantly correlated with the IPSS-ST (r=0.326, p<0.001), IPSS-VD (r=0.183, p=0.005), IPSS-total (r=0.310, p<0.001), and IIEF-5 total (r=-0.248, p<0.001).
Conclusions: LUTS, especially storage symptoms, were related to PE. In elderly men, control of both erectile dysfunction and LUTS may play an important role in managing PE.
Keywords: Ejaculation; Korean; Sexual dysfunction; Urinary symptoms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Premature ejaculation in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms: a systematic review.Int J Impot Res. 2021 Jul;33(5):516-524. doi: 10.1038/s41443-020-0298-5. Epub 2020 May 11. Int J Impot Res. 2021. PMID: 32393845
-
Associations between premature ejaculation, lower urinary tract symptoms, and erectile dysfunction in middle-aged Korean policemen.J Sex Med. 2014 Jun;11(6):1512-8. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12461. Epub 2014 Feb 17. J Sex Med. 2014. PMID: 24528521
-
[Correlation between premature ejaculation diagnostic tool and International Index of Erectile Function-15 in different types of premature ejaculation].Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2016 Sep;22(9):777-781. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2016. PMID: 29071872 Chinese.
-
Lower urinary tract symptoms and depressive symptoms among patients presenting for distressing early ejaculation.Int J Impot Res. 2020 Mar;32(2):207-212. doi: 10.1038/s41443-019-0147-6. Epub 2019 Apr 25. Int J Impot Res. 2020. PMID: 31024115
-
Effects of tamsulosin on premature ejaculation in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia.World J Mens Health. 2014 Aug;32(2):99-104. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.2014.32.2.99. Epub 2014 Aug 26. World J Mens Health. 2014. PMID: 25237660 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prevalence and factor association of premature ejaculation among adult Asian males with lower urinary tract symptoms.Prostate Int. 2015 Jun;3(2):65-9. doi: 10.1016/j.prnil.2015.03.001. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Prostate Int. 2015. PMID: 26157771 Free PMC article.
-
Premature ejaculation in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms: a systematic review.Int J Impot Res. 2021 Jul;33(5):516-524. doi: 10.1038/s41443-020-0298-5. Epub 2020 May 11. Int J Impot Res. 2021. PMID: 32393845
References
-
- Rosen RC, Wei JT, Althof SE, Seftel AD, Miner M, Perelman MA, et al. Association of sexual dysfunction with lower urinary tract symptoms of BPH and BPH medical therapies: results from the BPH Registry. Urology. 2009;73:562–566. - PubMed
-
- Laumann EO, Paik A, Rosen RC. Sexual dysfunction in the United States: prevalence and predictors. JAMA. 1999;281:537–544. - PubMed
-
- Chung TG, Lee TK, Chung S, Lee MS, Kim YS, Ahn TY. The Korean version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF): reliability and validation study. Korean J Urol. 1999;40:1334–1343.
-
- Kam SC, Han DH, Huh JH, Lee SW. Development and validation of a Korean version of the premature ejaculation diagnostic tool (PEDT) Korean J Androl. 2009;27:185–193.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources