The importance of the vaginal delivery route for antiretrovirals in HIV prevention
- PMID: 22468220
- PMCID: PMC3314337
- DOI: 10.4155/tde.11.126
The importance of the vaginal delivery route for antiretrovirals in HIV prevention
Abstract
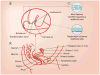
The HIV/AIDS pandemic continues to be a global health priority, with high rates of new HIV-I infections persisting in young women. One HIV prevention strategy is topical pre-exposure prophylactics or microbicides, which are applied vaginally or rectally to protect the user from HIV and possibly other sexually transmitted infections. Vaginal microbicide delivery will be the focus of this review. Multiple nonspecific and specific antiretroviral microbicide products have been clinically evaluated, and many are in preclinical development, The events of HIV mucosal transmission and dynamics of the cervicovaginal environment should be considered for successful vaginal microbicide delivery. Beyond conventional vaginal formulations, intravaginal rings, tablets and films are employed as platforms in the hope to increase the likelihood of microbicide use. Furthermore, combining multiple antiretrovirals within a given formulation, combining a microbicide product with a vaginal device and integrating novel drug-delivery strategies within a microbicide product are approaches to successful vaginal-microbicide delivery.
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS. AIDS Epidemic Update: December 2009. Joint UN Programme on HIV/AIDS; Geneva, Switzerland: 2009.
-
- Celentano DD, Nelson KE, Lyles CM, et al. Decreasing incidence of HIV and sexually transmitted diseases in young Thai men: evidence for success of the HIV/AIDS control and prevention program. AIDS. 1998;12(5):F29–F36. - PubMed
Websites
-
- Microbicides Trials Network. [Accessed 30 May 2011];Clinical Studies. www.mtnstopshiv.org.
-
- Global Advocacy for HIV Prevention. [Accessed 3 June 2011];Microbicides Clinical Trials. www.avac.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
