Templates for rejection: configuring attention to ignore task-irrelevant features
- PMID: 22468723
- PMCID: PMC3817824
- DOI: 10.1037/a0027885
Templates for rejection: configuring attention to ignore task-irrelevant features
Abstract
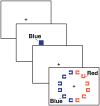
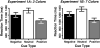
Theories of attention are compatible with the idea that we can bias attention to avoid selecting objects that have known nontarget features. Although this may underlie several existing phenomena, the explicit guidance of attention away from known nontargets has yet to be demonstrated. Here we show that observers can use feature cues (i.e., color) to bias attention away from nontarget items during visual search. These negative cues were used to quickly instantiate a template for rejection that reliably facilitated search across the cue-to-search stimulus onset asynchronies (SOAs), although negative cues were not as potent as cues that guide attention toward target features. Furthermore, by varying the search set size we show a template for rejection is increasingly effective in facilitating search as scene complexity increases. Our findings demonstrate that knowing what not to look for can be used to configure attention to avoid certain features, complimenting what is known about setting attention to select certain target features.
Figures
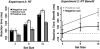

References
-
- Bundesen C. A theory of visual attention. Psychological Review. 1990;97:523–547. - PubMed
-
- Bundesen C, Habekost T, Kyllingsbaek S. A neural theory of visual attention: Bridging cognition and neurophysiology. Psychological Review. 2005;112:291–328. - PubMed
-
- Desimone R, Duncan J. Neural mechanisms of selective visual attention. Annual Review of Neuroscience. 1995;18:193–222. - PubMed
-
- James W. The Principles of Psychology. New York: Holt; 1890.
-
- Jiang Y, Chun M, Marks LE. Visual marking: Dissociating effects of new and old set size. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory & Cognition. 2002;28:293–302. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

