Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α-AA-modified bone marrow stem cells protect PC12 cells from hypoxia-induced apoptosis, partially through VEGF/PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 pathway
- PMID: 22468883
- PMCID: PMC3438847
- DOI: 10.1089/scd.2011.0604
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α-AA-modified bone marrow stem cells protect PC12 cells from hypoxia-induced apoptosis, partially through VEGF/PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 pathway
Abstract
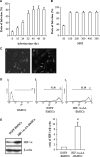
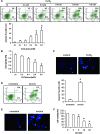
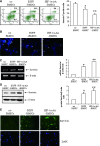
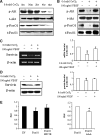
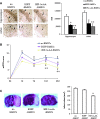
Bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs) have been shown to improve neurological function recovery in cerebral ischemia. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) α-AA is a more stable mutant form of HIF-1α, which is a crucial oxygen-sensitive regulator. To investigate the protective effects of HIF-1α-AA-modified BMSCs on neuron survival in cerebral ischemia models, we co-cultured HIF-1α-AA-modified BMSCs with neuron-like cells (PC12 cells) and observed a significant increase in the release of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) from BMSCs, the decreased PC12 cell apoptosis, and the upregulation of Survivin expression reduced by hypoxia in PC12 cells compared to enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) BMSCs. In addition, to explore whether VEGF secreted by HIF-1α-AA-modified BMSCs plays an important role in preventing hypoxia-induced apoptosis and the possible mechanism involved, exogenous VEGF were applied and the similar protective effects on PC12 cells were observed in vitro. Furthermore, hypoxia reduced the expression of phosphorylated Akt and phosphorylated FoxO1, whereas the administration of VEGF reversed these changes. Transfection of FoxO1 H215R, a DNA-binding mutant, abrogated the inhibitory ability on Survivin promoter activity, whereas FoxO1 AAA, the active form of FoxO1, presented further repression on Survivin promoter, indicating that FoxO1 directly binds on Survivin promoter as a transcriptional repressor and that phosphorylation status of FoxO1 affects its inhibition on the Survivin promoter. Transplantation of HIF-1α-AA-modified BMSCs after cerebral ischemia in vivo sufficiently reduced neurons apoptosis, decreased cerebral infarction volume, and induced a significant improvement on the modified neurological severity score compared to the EGFP BMSCs group. In conclusion, HIF-1α-AA-modified MSCs showed an obvious protective effect on neuron-like cells or neuron after ischemia in vitro and in vivo, at least in part, through the VEGF/PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 pathway.
Figures

References
-
- Donnan GA. Fisher M. Macleod M. Davis SM. Stroke. Lancet. 2008;371:1612–1623. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization The world health report 2004. Annex Table 2: Deaths by cause, sex, and mortality stratum in WHO regions, estimates for 2002. 2004.
-
- Lu J. Moochhala S. Moore XL. Ng KC. Tan MH. Lee LK. He B. Wong MC. Ling EA. Adult bone marrow cells differentiate into neural phenotypes and improve functional recovery in rats following traumatic brain injury. Neurosci Lett. 2006;398:12–17. - PubMed
-
- Chen X. Li Y. Wang L. Katakowski M. Zhang L. Chen J. Xu Y. Gautam SC. Chopp M. Ischemic rat brain extracts induce human marrow stromal cell growth factor production. Neuropathology. 2002;22:275–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

