Identification and functional screening of microRNAs highly deregulated in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 22469014
- PMCID: PMC4118234
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2012.01579.x
Identification and functional screening of microRNAs highly deregulated in colorectal cancer
Abstract
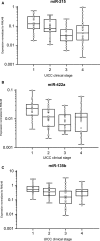
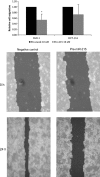
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) constitute a robust regulatory network with post-transcriptional regulatory efficiency for almost one half of human coding genes, including oncogenes and tumour suppressors. We determined the expression profile of 667 miRNAs in colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues and paired non-tumoural tissues and identified 42 differentially expressed miRNAs. We chose miR-215, miR-375, miR-378, miR-422a and miR-135b for further validation on an independent cohort of 125 clinically characterized CRC patients and for in vitro analyses. MiR-215, miR-375, miR-378 and miR-422a were significantly decreased, whereas miR-135b was increased in CRC tumour tissues. Levels of miR-215 and miR-422a correlated with clinical stage. MiR-135b was associated with higher pre-operative serum levels of CEA and CA19-9. In vitro analyses showed that ectopic expression of miR-215 decreases viability and migration, increases apoptosis and promotes cell cycle arrest in DLD-1 and HCT-116 colon cancer cell lines. Similarly, overexpression of miR-375 and inhibition of miR-135b led to decreased viability. Finally, restoration of miR-378, miR-422a and miR-375 inhibited G1/S transition. These findings indicate that miR-378, miR-375, miR-422a and miR-215 play an important role in CRC as tumour suppressors, whereas miR-135b functions as an oncogene; both groups of miRNA contribute to CRC pathogenesis.
© 2012 The Authors Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine © 2012 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, et al. Cancer statistics, 2011. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:212–36. - PubMed
-
- Janga SC, Vallabhaneni S. MicroRNAs as post-transcriptional machines and their interplay with cellular networks. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;722:59–74. - PubMed
-
- Slaby O, Svoboda M, Fabian P, et al. Altered expression of miR-21, miR-31, miR-143 and miR-145 is related to clinicopathologic features of colorectal cancer. Oncology. 2007;72:397–402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

