Naucline, a new indole alkaloid from the bark of Nauclea officinalis
- PMID: 22469596
- PMCID: PMC6268295
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules17044028
Naucline, a new indole alkaloid from the bark of Nauclea officinalis
Abstract
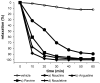
A new indole alkaloid, naucline (1) together with four known alkaloids, angustine (2), angustidine (3), nauclefine (4) and naucletine (5), were isolated from the bark of Nauclea officinalis. The structures of all isolated compounds were elucidated with various spectroscopic methods such as 1D- and 2D- NMR, IR, UV and LCMS-IT-TOF. In addition to that of alkaloid 1, the complete 13C-NMR data of naucletine (5) were also reported. Naucline (1) showed a moderate vasorelaxant activity (90% relaxation at 1 × 10(-5) M) whereas, angustine (2), nauclefine (4), and naucletine (5) showed potent vasorelaxant activity (more than 90% relaxation at 1 × 10(-5) M) on an isolated rat aorta.
Figures


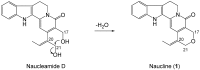
References
-
- Rova T.H.E., Delprete P.G., Andersson L., Albert V.A. A trnL-F cpDNA sequence study of the condamineeae-rondeletieae-sipaneeae complex with implications on the phylogeny of the rubiaceae. Am. J. Bot. 2002;89:145–159. - PubMed
-
- Mongrand S., Badoc A., Patouille B., Lacomblez C., Chavent M., Bessoule J.-J. Chemotaxonomy of Rubiaceae family based on leaf fatty acid composition. Phytochemistry. 2005;66:549–559. - PubMed
-
- Burn E.N., Taiwe G.S., Moto F.C.O., Ngoupaye G.T., Nkantchoua G.C.N., Pelanken M.M., Rakotonirina S.V., Rakotonirina A. Anticonvulsant, anxioloytic, and sedative propertives of the roots of Nauclea latifolia Smith in mice. Epilepsy Behav. 2009;15:434–440. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2009.05.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Okoro I.O., Osagie A., Asibor E.O. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of polyphenols from ethanomedicinal plants of Nigeria. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010;9:2989–2993.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

