Targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: novel agents on the horizon
- PMID: 22470194
- PMCID: PMC3359882
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.466
Targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: novel agents on the horizon
Abstract
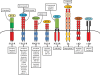
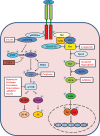
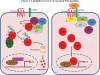
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common liver cancer, accounting for 90% of primary liver cancers. In the last decade it has become one of the most frequently occurring tumors worldwide and is also considered to be the most lethal of the cancer systems, accounting for approximately one third of all malignancies. Although the clinical diagnosis and management of early-stage HCC has improved significantly, HCC prognosis is still extremely poor. Furthermore, advanced HCC is a highly aggressive tumor with a poor or no response to common therapies. Therefore, new effective and well-tolerated therapy strategies are urgently needed. Targeted therapies have entered the field of anti-neoplastic treatment and are being used on their own or in combination with conventional chemotherapy drugs. Molecular-targeted therapy holds great promise in the treatment of HCC. A new therapeutic opportunity for advanced HCC is the use of sorafenib (Nexavar). On the basis of the recent large randomized phase III study, the Sorafenib HCC Assessment Randomized Protocol (SHARP), sorafenib has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of advanced HCC. Sorafenib showed to be able to significantly increase survival in patients with advanced HCC, establishing a new standard of care. Despite this promising breakthrough, patients with HCC still have a dismal prognosis, as it is currently the major cause of death in cirrhotic patients. Nevertheless, the successful results of the SHARP trial underscore the need for a comprehensive understanding of the molecular pathogenesis of this devastating disease. In this review we summarize the most important studies on the signaling pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of HCC, as well as the newest emerging drugs and their potential use in HCC management.
Figures
References
-
- Montalto G, Cervello M, Giannitrapani L, D'Antona F, Terranova A, Castagnetta LM. Epidemiology, risk factors and natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;963:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;362:1907–1917. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Whelan SL, Ferlay J, Teppo L, Thomas DB, editors. IARC, Scientific Publications Nº 155; Lyon: 2002. Cancer Incidence In Five Continents. Vol. VIII; pp. 1–782.
-
- Schütte K, Bornschein J, Malfertheiner P. Hepatocellular carcinoma--epidemiological trends and risk factors. Dig Dis. 2009;27:80–92. - PubMed
-
- Chang MH, Chen CJ, Lai MS, Hsu HM, Wu TC, Kong MS, Liang DC, Shau WY, Chen DS. Universal hepatitis B vaccination in Taiwan and the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in children. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1855–1859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

