Inhibitory effect of statins on inflammatory cytokine production from human bronchial epithelial cells
- PMID: 22471285
- PMCID: PMC3390525
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2012.04564.x
Inhibitory effect of statins on inflammatory cytokine production from human bronchial epithelial cells
Abstract
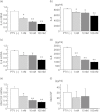
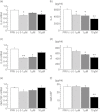
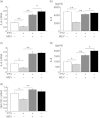
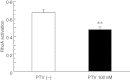
Statins are 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-co-enzyme A reductase inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis, and have been reported to exert pleiotropic effects on cellular signalling and cellular functions involved in inflammation. Recent reports have demonstrated that previous statin therapy reduced the risk of pneumonia or increased survival in patients with community-acquired pneumonia. However, the precise mechanisms responsible for these effects are unclear. In the present study, we examined the effects of statins on cytokine production from lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B). Interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 mRNA expression and protein secretion in LPS-stimulated cells were inhibited significantly by the lipophilic statin pitavastatin and the hydrophilic statin pravastatin. As these inhibitory effects of statin were negated by adding mevalonate, the anti-inflammatory effects of statins appear to be exerted via the mevalonic cascade. In addition, the activation levels of Ras homologue gene family A (RhoA) in BEAS-2B cells cultured with pitavastatin were significantly lower than those without the statin. These results suggest that statins have anti-inflammatory effects by reducing cytokine production through inhibition of the mevalonic cascade followed by RhoA activation in the lung.
© 2012 The Authors;Clinical and Experimental Immunology © 2012 British Society for Immunology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lipophilic but not hydrophilic statins selectively induce cell death in gynaecological cancers expressing high levels of HMGCoA reductase.J Cell Mol Med. 2010 May;14(5):1180-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00771.x. Epub 2009 May 11. J Cell Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 19432822 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effects of pitavastatin on fibrogenic mediator production by human lung fibroblasts.Life Sci. 2013 Dec 18;93(25-26):968-74. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2013.10.026. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 24211780
-
Cardioprotective cytokine interleukin-33 is up-regulated by statins in human cardiac tissue.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Dec;22(12):6122-6133. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13891. Epub 2018 Sep 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30216659 Free PMC article.
-
The role of pleiotropic effects of statins in dementia.Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 2006;185:115-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.2006.00695.x. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 2006. PMID: 16866920 Review.
-
Statins and cancer development.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005 Aug;14(8):1897-8. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-05-0027. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005. PMID: 16103434 Review.
Cited by
-
Statin and aspirin as adjuvant therapy in hospitalised patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a randomised clinical trial (RESIST trial).BMC Infect Dis. 2022 Jul 9;22(1):606. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07570-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35810307 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Statin use and asthma control in patients with severe asthma.BMJ Open. 2013 Aug 13;3(8):e003314. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003314. BMJ Open. 2013. PMID: 23943778 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Statins on the Risk of Poststroke Pneumonia: National Population-Based Cohort Study.Infect Drug Resist. 2020 Aug 6;13:2689-2698. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S258420. eCollection 2020. Infect Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 32982323 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of inflammation, oxidative stress, and vascular dysfunction in hypertension.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:406960. doi: 10.1155/2014/406960. Epub 2014 Jul 20. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25136585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pleiotropic effects of the hydroxy-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors in renal disease.Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2014 Mar 28;7:123-30. doi: 10.2147/IJNRD.S55102. eCollection 2014. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2014. PMID: 24729724 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gaw A. A new reality: achieving cholesterol-lowering goals in clinical practice. Atheroscler Suppl. 2002;2:5–8. discussion 8–11. - PubMed
-
- Jain MK, Ridker PM. Anti-inflammatory effects of statins: clinical evidence and basic mechanisms. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4:977–87. - PubMed
-
- Yamada T, Node K, Mine T, et al. Long-term effect of atorvastatin on neurohumoral activation and cardiac function in patients with chronic heart failure: a prospective randomized controlled study. Am Heart J. 2007;153:1055. e1051–8. - PubMed
-
- Alber HF, Frick M, Sussenbacher A, et al. Effect of atorvastatin on peripheral endothelial function and systemic inflammatory markers in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2007;157:73–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

