Comparison of (64)Cu-complexing bifunctional chelators for radioimmunoconjugation: labeling efficiency, specific activity, and in vitro/in vivo stability
- PMID: 22471317
- PMCID: PMC4756438
- DOI: 10.1021/bc300037w
Comparison of (64)Cu-complexing bifunctional chelators for radioimmunoconjugation: labeling efficiency, specific activity, and in vitro/in vivo stability
Abstract
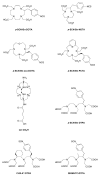
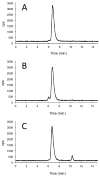
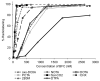
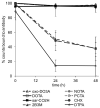
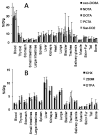
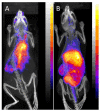
High radiolabeling efficiency, preferably to high specific activity, and good stability of the radioimmunoconjugate are essential features for a successful immunoconjugate for imaging or therapy. In this study, the radiolabeling efficiency, in vitro stability, and biodistribution of immunoconjugates with eight different bifunctional chelators labeled with (64)Cu were compared. The anti-CD20 antibody, rituximab, was conjugated to four macrocyclic bifunctional chelators (p-SCN-Bn-DOTA, p-SCN-Bn-Oxo-DO3A, p-SCN-NOTA, and p-SCN-PCTA), three DTPA derivatives (p-SCN-Bn-DTPA, p-SCN-CHX-A″-DTPA, and ITC-2B3M-DTPA), and a macrobicyclic hexamine (sarcophagine) chelator (sar-CO2H) = (1-NH2-8-NHCO(CH2)3CO2H)sar where sar = sarcophagine = 3,6,10,13,16,19-hexaazabicyclo[6.6.6]icosane). Radiolabeling efficiency under various conditions, in vitro stability in serum at 37 °C, and in vivo biodistribution and imaging in normal mice over 48 h were studied. All chelators except sar-CO2H were conjugated to rituximab by thiourea bond formation with an average of 4.9 ± 0.9 chelators per antibody molecule. Sar-CO2H was conjugated to rituximab by amide bond formation with 0.5 chelators per antibody molecule. Efficiencies of (64)Cu radiolabeling were dependent on the concentration of immunoconjugate. Notably, the (64)Cu-NOTA-rituximab conjugate demonstrated the highest radiochemical yield (95%) under very dilute conditions (31 nM NOTA-rituximab conjugate). Similarly, sar-CO-rituximab, containing 1/10th the number of chelators per antibody compared to that of other conjugates, retained high labeling efficiency (98%) at an antibody concentration of 250 nM. In contrast to the radioimmunoconjugates containing DTPA derivatives, which demonstrated poor serum stability, all macrocyclic radioimmunoconjugates were very stable in serum with <6% dissociation of (64)Cu over 48 h. In vivo biodistribution profiles in normal female Balb/C mice were similar for all the macrocyclic radioimmunoconjugates with most of the activity remaining in the blood pool up to 48 h. While all the macrocyclic bifunctional chelators are suitable for molecular imaging using (64)Cu-labeled antibody conjugates, NOTA and sar-CO2H show significant advantages over the others in that they can be radiolabeled rapidly at room temperature, under dilute conditions, resulting in high specific activity.
Figures
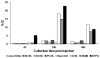
Similar articles
-
Improved Conjugation, 64-Cu Radiolabeling, in Vivo Stability, and Imaging Using Nonprotected Bifunctional Macrocyclic Ligands: Bis(Phosphinate) Cyclam (BPC) Chelators.J Med Chem. 2018 Oct 11;61(19):8774-8796. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00932. Epub 2018 Sep 24. J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30180567
-
Copper-64 radiolabeling and biological evaluation of bifunctional chelators for radiopharmaceutical development.Nucl Med Biol. 2012 Nov;39(8):1099-104. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2012.05.009. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Nucl Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22743158 Free PMC article.
-
An improved synthesis and biological evaluation of a new cage-like bifunctional chelator, 4-((8-amino-3,6,10,13,16,19-hexaazabicyclo[6.6.6]icosane-1-ylamino)methyl)benzoic acid, for 64Cu radiopharmaceuticals.Nucl Med Biol. 2010 Jan;37(1):57-65. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2009.09.001. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Nucl Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20122669
-
Labeling biomolecules with radiorhenium: a review of the bifunctional chelators.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2007 May;7(3):367-77. doi: 10.2174/187152007780618144. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17504162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping biological behaviors by application of longer-lived positron emitting radionuclides.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013 Jul;65(8):1098-111. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.10.012. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013. PMID: 23123291 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of PET Radioisotope Copper-64-Labeled Theranostic Immunoliposomes for EGFR Overexpressing Cancer-Targeted Therapy and Imaging.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 2;25(3):1813. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031813. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339090 Free PMC article.
-
Positron emission tomography imaging of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor expression with (61)Cu-labeled lysine-tagged VEGF121.Mol Pharm. 2012 Dec 3;9(12):3586-94. doi: 10.1021/mp3005269. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Mol Pharm. 2012. PMID: 23137334 Free PMC article.
-
Site-specific chelator-antibody conjugation for PET and SPECT imaging with radiometals.Drug Discov Today Technol. 2018 Dec;30:91-104. doi: 10.1016/j.ddtec.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2018. PMID: 30553525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
⁶⁴Cu-labeled inhibitors of prostate-specific membrane antigen for PET imaging of prostate cancer.J Med Chem. 2014 Mar 27;57(6):2657-69. doi: 10.1021/jm401921j. Epub 2014 Mar 7. J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24533799 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive positron emission tomography and fluorescence imaging of CD133+ tumor stem cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Feb 11;111(6):E692-701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1314189111. Epub 2014 Jan 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24469819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meares CF, Goodwin DA. Linking radiometals to proteins with bifuntional chelating agents. J. Protein Chem. 1984;3:215–28.
-
- Blower PJ, Lewis JS, Zweit J. Copper radionuclides and radiopharmaceuticals in nuclear medicine. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1996;23:957–80. - PubMed
-
- Donnelly PS. The role of coordination chemistry in the development of copper and rhenium radiopharmaceuticals. Dalton Trans. 2011;40:999–1010. - PubMed
-
- Zamora PO, Mercer-Smith JA, Marek MJ, Schulte LD, Rhodes BA. Similarity of copper and technetium binding sites in human IgG. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1992;19:797–802. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

